A Special Extract of Bacopa monnieri (CDRI-08) Restores Learning and Memory by Upregulating Expression of the NMDA Receptor Subunit GluN2B in the Brain of Scopolamine-Induced Amnesic Mice
- PMID: 26413117
- PMCID: PMC4564605
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/254303
A Special Extract of Bacopa monnieri (CDRI-08) Restores Learning and Memory by Upregulating Expression of the NMDA Receptor Subunit GluN2B in the Brain of Scopolamine-Induced Amnesic Mice
Abstract
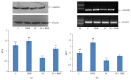
In the present communication, we have investigated effects of the CDRI-08, a well characterized extract of Bacopa monnieri, on expression of the GluN2B subunit of NMDAR in various brain regions of the scopolamine-induced amnesic mice. Our behavioral data reveal that scopolamine-treated amnesic mice exhibit significant decline in the spatial memory compared to the normal control mice. Our RT-PCR and immunoblotting data revealed that the scopolamine treatment resulted in a significant downregulation of the NMDAR GluN2B subunit expression in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Our enzyme assay data revealed that scopolamine caused a significant increase in the acetylcholinesterase activity in both the brain regions. Further, oral administration of the CDRI-08 to scopolamine-treated amnesic mice restored the spatial memory which was found to be associated with significant upregulation of the GluN2B subunit expression and decline in the acetylcholinesterase activity in prefrontal cortex as well as hippocampus towards their levels in the normal control mice. Our study provides the evidence for the mechanism underlying role of the Bacopa monnieri extract (CDRI-08) in restoring spatial memory in amnesic mice, which may have therapeutic implications.
Figures





References
-
- Gazzaniga M. S., Ivry R. B., Mangun G. R. Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind. Norton; 2009.
-
- Lerner K. L., Lerner B. W. Gale Encyclopedia of Science. Gale; 2004.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

