Implementation and Operational Research: Programmatic Feasibility of Dried Blood Spots for the Virological Follow-up of Patients on Antiretroviral Treatment in Nord Kivu, Democratic Republic of the Congo
- PMID: 26413848
- PMCID: PMC4679362
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000000844
Implementation and Operational Research: Programmatic Feasibility of Dried Blood Spots for the Virological Follow-up of Patients on Antiretroviral Treatment in Nord Kivu, Democratic Republic of the Congo
Abstract
Background: As part of its policy to shift monitoring of antiretroviral therapy (ART) to primary health care (PHC) workers, the Ministry of Health of the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) tested the feasibility of using dried blood spots (DBS) for viral load (VL) quantification and genotypic drug resistance testing in off-site high-throughput laboratories.
Methods: DBS samples from adults on ART were collected in 13 decentralized PHC facilities in the Nord-Kivu province and shipped during program quarterly supervision to a reference laboratory 2000 km away, where VL was quantified with a commercial assay (m2000rt, Abbott). A second DBS was sent to a World Health Organization (WHO)-accredited laboratory for repeat VL quantification on a subset of samples with a generic assay (Biocentric) and genotypic drug resistance testing when VL >1000 copies per milliliter.
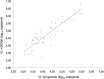
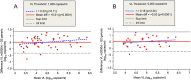
Findings: Constraints arose because of an interruption in national laboratory funding rather than to technical or logistic problems. All samples were assessed by both VL assays to allow ART adjustment. Median DBS turnaround time was 37 days (interquartile range: 9-59). Assays performed unequally with DBS, impacting clinical decisions, quality assurance, and overall cost-effectiveness. Based on m2000rt or generic assay, 31.3% of patients were on virological failure (VF) and 14.8% presented resistance mutations versus 50.3% and 15.4%, respectively.
Conclusion: This study confirms that current technologies involving DBS make virological monitoring of ART possible at PHC level, including in challenging environments, provided organizational issues are addressed. Adequate core funding of HIV laboratories and adapted choice of VL assays require urgent attention to control resistance to ART as coverage expands.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Field evaluation of dried blood spots for routine HIV-1 viral load and drug resistance monitoring in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy in Africa and Asia.J Clin Microbiol. 2014 Feb;52(2):578-86. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02860-13. Epub 2013 Dec 11. J Clin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24478491 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of dried blood spots for HIV viral load monitoring in decentralized area in North Vietnam in a test-and-treat era, the MOVIDA project.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 9;15(4):e0230968. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230968. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32271796 Free PMC article.
-
High efficacy of first-line ART in a West African cohort, assessed by dried blood spot virological and pharmacological measurements.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016 Nov;71(11):3222-3227. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkw286. Epub 2016 Jul 20. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27439522
-
Dried blood spots can expand access to virological monitoring of HIV treatment in resource-limited settings.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009 Dec;64(6):1126-9. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp353. Epub 2009 Sep 23. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19776036 Review.
-
Measurement of HIV-1 viral load for drug resistance surveillance using dried blood spots: literature review and modeling of contribution of DNA and RNA.AIDS Rev. 2014 Jul-Sep;16(3):160-71. AIDS Rev. 2014. PMID: 25221990 Review.
Cited by
-
High drug resistance levels could compromise the control of HIV infection in paediatric and adolescent population in Kinshasa, the Democratic Republic of Congo.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 15;16(4):e0248835. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248835. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33857166 Free PMC article.
-
The feasibility of fingerstick blood collection for point-of-care HIV-1 viral load monitoring in rural Zambia.Glob Health Innov. 2018;1(2):3. doi: 10.15641/ghi.v1i2.585. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Glob Health Innov. 2018. PMID: 30734030 Free PMC article.
-
Resource and infrastructure challenges on the RESIST-2 Trial: an implementation study of drug resistance genotype-based algorithmic ART switches in HIV-2-infected adults in Senegal.Trials. 2021 Dec 18;22(1):931. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05902-5. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34922614 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
HIV-1 subtypes and drug resistance mutations among female sex workers varied in different cities and regions of the Democratic Republic of Congo.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 11;15(2):e0228670. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228670. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32045455 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent HIV-1 strains (CRF92_C2U and CRF93_cpx) co-circulating in the Democratic Republic of the Congo: Phylogenetic insights on the early evolutionary history of subtype C.Virus Evol. 2017 Nov 10;3(2):vex032. doi: 10.1093/ve/vex032. eCollection 2017 Jul. Virus Evol. 2017. PMID: 29250430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The Union. Management of Tuberculosis. A Guide to the Essentials of Good Practice. 6th ed Paris, France: IUATLD; 2010. Available at: http://www.theunion.org/what-we-do/publications/technical/management-of-.... Accessed February 24, 2015.
-
- World Health Organization. Task Shifting: Rational Redistribution of Tasks Among Health Workforce Teams. Geneva, Switzerland: 2008. Available at: http://www.who.int/healthsystems/TTR-TaskShifting.pdf. Accessed February 24, 2015.
-
- World Health Organization. Consolidated Guidelines on the Use of Antiretroviral Drugs for Treating and Preventing HIV Infection. Recommendations for a Public Health Approach. Geneva, Switzerland: 2013. Available at: http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/guidelines/arv2013/download/en/. Accessed February 24, 2015. - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS. HIV and AIDS estimates (2013). Available at: http://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/democraticrepublicof.... Accessed February 20, 2015.
-
- Johannessen A. Dried blood spots in HIV monitoring: applications in resource-limited settings. Bioanalysis. 2010;2:1893–1908. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

