Conducting Polymers for Neural Prosthetic and Neural Interface Applications
- PMID: 26414302
- PMCID: PMC4681501
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.201501810
Conducting Polymers for Neural Prosthetic and Neural Interface Applications
Abstract
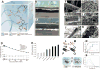
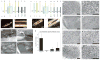
Neural-interfacing devices are an artificial mechanism for restoring or supplementing the function of the nervous system, lost as a result of injury or disease. Conducting polymers (CPs) are gaining significant attention due to their capacity to meet the performance criteria of a number of neuronal therapies including recording and stimulating neural activity, the regeneration of neural tissue and the delivery of bioactive molecules for mediating device-tissue interactions. CPs form a flexible platform technology that enables the development of tailored materials for a range of neuronal diagnostic and treatment therapies. In this review, the application of CPs for neural prostheses and other neural interfacing devices is discussed, with a specific focus on neural recording, neural stimulation, neural regeneration, and therapeutic drug delivery.
Keywords: conducting polymers; neural interfaces; neural recording; neural stimulation.
© 2015 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

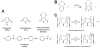




References
-
- Wark HAC, Sharma R, Mathews KS, Fernandez E, Yoo J, Christensen B, Tresco P, Rieth L, Solzbacher F, Normann RA, Tathireddy P. A new high-density (25 electrodes/mm 2 ) penetrating microelectrode array for recording and stimulating sub-millimeter neuroanatomical structures. Journal of Neural Engineering. 2013;10:045003. - PubMed
-
- Venkatraman S, Hendricks J, King ZA, Sereno AJ, Richardson-Burns S, Martin D, Carmena JM. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of PEDOT Microelectrodes for Neural Stimulation and Recording. Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, IEEE Transactions on. 2011;19:307–316. - PubMed
-
- Ludwig KA, Uram JD, Yang J, Martin DC. Chronic neural recordings using silicon microelectrode arrays electrochemically deposited with poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) film. J Neural Eng. 2006;3:59–70. - PubMed
-
- Kim D-H, Wiler JA, Anderson DJ, Kipke DR, Martin DC. Conducting polymers on hydrogel-coated neural electrode provide sensitive neural recordings in auditory cortex. Acta Biomaterialia. 2010;6:57–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

