An atlas of genetic correlations across human diseases and traits
- PMID: 26414676
- PMCID: PMC4797329
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3406
An atlas of genetic correlations across human diseases and traits
Abstract
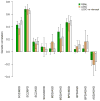
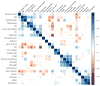
Identifying genetic correlations between complex traits and diseases can provide useful etiological insights and help prioritize likely causal relationships. The major challenges preventing estimation of genetic correlation from genome-wide association study (GWAS) data with current methods are the lack of availability of individual-level genotype data and widespread sample overlap among meta-analyses. We circumvent these difficulties by introducing a technique-cross-trait LD Score regression-for estimating genetic correlation that requires only GWAS summary statistics and is not biased by sample overlap. We use this method to estimate 276 genetic correlations among 24 traits. The results include genetic correlations between anorexia nervosa and schizophrenia, anorexia and obesity, and educational attainment and several diseases. These results highlight the power of genome-wide analyses, as there currently are no significantly associated SNPs for anorexia nervosa and only three for educational attainment.
References
-
- Smith George Davey, Ebrahim Shah. Mendelian randomization: can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? International journal of epidemiology. 2003;32(1):1–22. - PubMed
-
- Vandenberg SG. Multivariate analysis of twin differences. Methods and goals in human behavior genetics. 1965:29–43.
-
- Loehlin John C, Vandenberg Steven Gerritjan. Genetic and environmental components in the covariation of cognitive abilities: An additive model. Louisville Twin Study, University of Louisville; 1966.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01 AG012100/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 082604/2/07/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- AG081220/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 MH101244/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA173785/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG006399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 503480/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U106179472/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG033193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials