Partitioning heritability by functional annotation using genome-wide association summary statistics
- PMID: 26414678
- PMCID: PMC4626285
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3404
Partitioning heritability by functional annotation using genome-wide association summary statistics
Abstract
Recent work has demonstrated that some functional categories of the genome contribute disproportionately to the heritability of complex diseases. Here we analyze a broad set of functional elements, including cell type-specific elements, to estimate their polygenic contributions to heritability in genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of 17 complex diseases and traits with an average sample size of 73,599. To enable this analysis, we introduce a new method, stratified LD score regression, for partitioning heritability from GWAS summary statistics while accounting for linked markers. This new method is computationally tractable at very large sample sizes and leverages genome-wide information. Our findings include a large enrichment of heritability in conserved regions across many traits, a very large immunological disease-specific enrichment of heritability in FANTOM5 enhancers and many cell type-specific enrichments, including significant enrichment of central nervous system cell types in the heritability of body mass index, age at menarche, educational attainment and smoking behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing financial interests.
Figures


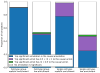
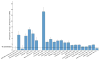
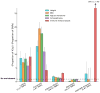

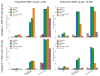
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 GM106584/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA173785/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG006399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA182821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U106179472/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 HG0070033/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR063759/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 MH101244/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007748/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- WT098051/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

