Diagnostic Accuracy of Digital Screening Mammography With and Without Computer-Aided Detection
- PMID: 26414882
- PMCID: PMC4836172
- DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.5231
Diagnostic Accuracy of Digital Screening Mammography With and Without Computer-Aided Detection
Abstract
Importance: After the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved computer-aided detection (CAD) for mammography in 1998, and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) provided increased payment in 2002, CAD technology disseminated rapidly. Despite sparse evidence that CAD improves accuracy of mammographic interpretations and costs over $400 million a year, CAD is currently used for most screening mammograms in the United States.
Objective: To measure performance of digital screening mammography with and without CAD in US community practice.
Design, setting, and participants: We compared the accuracy of digital screening mammography interpreted with (n = 495 818) vs without (n = 129 807) CAD from 2003 through 2009 in 323 973 women. Mammograms were interpreted by 271 radiologists from 66 facilities in the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium. Linkage with tumor registries identified 3159 breast cancers in 323 973 women within 1 year of the screening.
Main outcomes and measures: Mammography performance (sensitivity, specificity, and screen-detected and interval cancers per 1000 women) was modeled using logistic regression with radiologist-specific random effects to account for correlation among examinations interpreted by the same radiologist, adjusting for patient age, race/ethnicity, time since prior mammogram, examination year, and registry. Conditional logistic regression was used to compare performance among 107 radiologists who interpreted mammograms both with and without CAD.
Results: Screening performance was not improved with CAD on any metric assessed. Mammography sensitivity was 85.3% (95% CI, 83.6%-86.9%) with and 87.3% (95% CI, 84.5%-89.7%) without CAD. Specificity was 91.6% (95% CI, 91.0%-92.2%) with and 91.4% (95% CI, 90.6%-92.0%) without CAD. There was no difference in cancer detection rate (4.1 in 1000 women screened with and without CAD). Computer-aided detection did not improve intraradiologist performance. Sensitivity was significantly decreased for mammograms interpreted with vs without CAD in the subset of radiologists who interpreted both with and without CAD (odds ratio, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.29-0.97).
Conclusions and relevance: Computer-aided detection does not improve diagnostic accuracy of mammography. These results suggest that insurers pay more for CAD with no established benefit to women.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
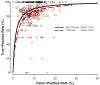
Comment in
-
Is It Time to Stop Paying for Computer-Aided Mammography?JAMA Intern Med. 2015 Nov;175(11):1837-8. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.5319. JAMA Intern Med. 2015. PMID: 26414612 No abstract available.
-
Computer aided mammography yields no clear benefit, research finds.BMJ. 2015 Sep 28;351:h5164. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h5164. BMJ. 2015. PMID: 26419394 No abstract available.
-
Potential Benefits of Computer-Aided Detection for Cancer Identification and Treatment.JAMA Intern Med. 2016 Mar;176(3):410. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.8459. JAMA Intern Med. 2016. PMID: 26954044 No abstract available.
-
Potential Benefits of Computer-Aided Detection for Cancer Identification and Treatment-Reply.JAMA Intern Med. 2016 Mar;176(3):411. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.8474. JAMA Intern Med. 2016. PMID: 26954046 No abstract available.
References
-
- Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data: R2 Technologies(P970058) U. S. Food and Drug Administration; 1998. p. 970058. http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/98fr/123098b.txt.
-
- Rao VM, Levin DC, Parker L, et al. How widely is computer-aided detection used in screening and diagnostic mammography? J Am Coll Radiol. 2010;7(10):802–5. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert FJ, Astley SM, McGeeMA, et al. Single reading with computer-aided detection and double reading of screening mammograms in the United Kingdom National Breast Screening Program. Radiology. 2006;241(1):47–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

