A Proposed Grading System to Standardize the Description of Renal Papillary Appearance at the Time of Endoscopy in Patients with Nephrolithiasis
- PMID: 26414908
- PMCID: PMC4744462
- DOI: 10.1089/end.2015.0298
A Proposed Grading System to Standardize the Description of Renal Papillary Appearance at the Time of Endoscopy in Patients with Nephrolithiasis
Abstract
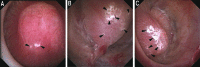
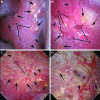
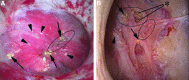
Background and purpose: The appearance of the renal papillae in patients with nephrolithiasis can be quite variable and can range from entirely healthy to markedly diseased. The implications of such findings remain unknown. One potential reason is the lack of a standardized system to describe such features. We propose a novel grading scale to describe papillary appearance at the time of renal endoscopy.
Methods: Comprehensive endoscopic renal assessment and mapping were performed on more than 300 patients with nephrolithiasis. Recurring abnormal papillary characteristics were identified and quantified based on degree of severity.
Results: Four unique papillary features were chosen for inclusion in the PPLA scoring system- ductal Plugging, Pitting, Loss of contour, and Amount of Randall's plaque. Unique scores are calculated for individual papillae based on reference examples.
Conclusions: The description and study of renal papillary appearance in stone formers have considerable potential as both a clinical and research tool; however, a standardized grading system is necessary before using it for these purposes.
Figures

References
-
- Evan AP, Lingeman J, Coe F, et al. . Renal histopathology of stone-forming patients with distal renal tubular acidosis. Kidney Int 2007;71:795–801 - PubMed
-
- Matlaga BR, Williams JC, Jr, Kim SC, et al. . Endoscopic evidence of calculus attachment to Randall's plaque. J Urol 2006;175:1720–1724 - PubMed
-
- Evan AE, Lingeman JE, Coe FL, et al. . Histopathology and surgical anatomy of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism and calcium phosphate stones. Kidney Int 2008;74:223–229 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

