Cytopathologic diagnosis of oncocytic type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: Criteria and clinical implications of accurate diagnosis
- PMID: 26415076
- PMCID: PMC4982396
- DOI: 10.1002/cncy.21627
Cytopathologic diagnosis of oncocytic type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: Criteria and clinical implications of accurate diagnosis
Abstract
Background: Cytologic findings of pancreatic oncocytic-type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs)/intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasms (IOPNs) are largely unknown.
Methods: Five IOPNs encountered by the authors were analyzed.
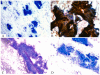
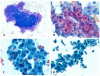
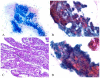
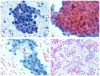
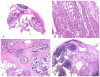
Results: Four IOPNs were located in the pancreatic head, and 1 was located in the pancreatic body/tail in 2 men and 3 women ages 56 to 84 years (mean age, 66 years). Radiologic diagnoses included pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) in 2 patients, invasive cancer associated with IPMN in 1 patient, IPMN versus mucinous cystic neoplasm in 1 patient, and cystic mass in 1 patient. Cytologic findings included: hypercellular smears (4 of 5 cases) containing well formed clusters of oncocytic cells (5 of 5 cases) with prominent, slightly eccentric nucleoli (4 of 5 cases), predominantly arranged in sheets/papillary units (5 of 5 cases), with punched-out intercytoplasmic spaces (4 of 5 cases), and with occasional 3-dimensional groups and focal necrosis (3 of 5 cases). The intracytoplasmic mucin and thick extracellular mucin typical of other IPMNs were observed only in 2 cases and were very limited. The mean size on resection was 4.5 cm. Invasion was observed in 3 cases (0.1, 0.3, and 2.0 cm) of tubular-type IPMN. Initial cytologic evaluation was performed by the authors in 4 of 5 cases, which were diagnosed as IOPN (n = 3) and IPMN versus cystic PDAC (n = 1). One case was initially misdiagnosed as PDAC and, on resection, proved to be noninvasive IOPN.
Conclusions: Cytologic features of IOPNs are classical, similar to their histologic counterparts, and differ significantly from other IPMN subtypes. Because of their highly complex appearance, they are often radiologically misdiagnosed as PDAC; thus, failure to recognize their characteristic features on fine-needle aspiration may lead to inappropriate treatment. Patients with IOPN have an incomparably better prognosis than patients with ordinary PDAC, even when their neoplasms are invasive.
Keywords: cytology; fine-needle aspiration; intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasm (IOPN); intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN); oncocytic; oncocytic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; pancreas.
© 2015 American Cancer Society.
Figures

References
-
- American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts & Figures 2015. American Cancer Society; Atlanta, GA: 2015. Available at: http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@editorial/documents/document/a.... Accessed February 18, 2015.
-
- Lee KS, Sekhar A, Rofsky NM, Pedrosa I. Prevalence of incidental pancreatic cysts in the adult population on MR imaging. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:2079–2084. - PubMed
-
- Kloppel G, Basturk O, Schlitter AM, Konukiewitz B, Esposito I. Intraductal neoplasms of the pancreas. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2014;31:452–466. - PubMed
-
- Adsay NV, Conlon KC, Zee SY, Brennan MF, Klimstra DS. Intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: an analysis of in situ and invasive carcinomas in 28 patients. Cancer. 2002;94:62–77. - PubMed
-
- Adsay NV, Merati K, Basturk O, et al. Pathologically and biologically distinct types of epithelium in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: delineation of an “intestinal” pathway of carcinogenesis in the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:839–848. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

