A Systematic Review of Experimental Strategies Aimed at Improving Motor Function after Acute and Chronic Spinal Cord Injury
- PMID: 26415105
- PMCID: PMC4779320
- DOI: 10.1089/neu.2014.3812
A Systematic Review of Experimental Strategies Aimed at Improving Motor Function after Acute and Chronic Spinal Cord Injury
Abstract
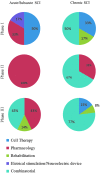
While various approaches have been proposed in clinical trials aimed at improving motor function after spinal cord injury in humans, there is still limited information regarding the scope, methodological quality, and evidence associated with single-intervention and multi-intervention approaches. A systematic review performed using the PubMed search engine and the key words "spinal cord injury motor recovery" identified 1973 records, of which 39 were selected (18 from the search records and 21 from reference list inspection). Study phase ( clinicaltrials.org criteria) and methodological quality (Cochrane criteria) were assessed. Studies included proposed a broad range of single-intervention (encompassing cell therapies, pharmacology, electrical stimulation, rehabilitation) (encompassing cell therapies, pharmacology, electrical stimulation, rehabilitation) and multi-intervention approaches (that combined more than one strategy). The highest evidence level was for Phase III studies supporting the role of multi-intervention approaches that contained a rehabilitation component. Quality appraisal revealed that the percentage of selected studies classified with high risk of bias by Cochrane criteria was as follows: random sequence generation = 64%; allocation concealment = 77%; blinding of participants and personnel = 69%; blinding of outcome assessment = 64%; attrition = 44%; selective reporting = 44%. The current literature contains a high proportion of studies with a limited ability to measure efficacy in a valid manner because of low methodological strength in all items of the Cochrane risk of bias assessment. Recommendations to decrease bias are discussed and include increased methodological rigor in the study design and recruitment of study participants, and the use of electrophysiological and imaging measures that can assess functional integrity of the spinal cord (and may be sufficiently sensitive to detect changes that occur in response to therapeutic interventions).
Keywords: cell transplantation; electrophysiology; human studies; rehabilitation; spinal cord injury.
Figures
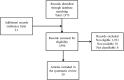
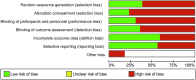
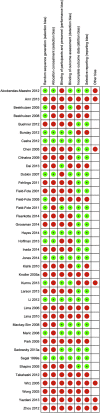
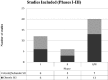
References
-
- National Spinal Cord Injury Statistical Center. Spinal cord injury: facts and figures at a glance. Birmingham, AL: Available at: nscisc.uab.edu Accessed: September10, 2015
-
- Fawcett J.W., Curt A., Steeves J.D., Coleman W.P., Tuszynski M.H., Lammertse D., Bartlett P.F., Blight A.R., Dietz V., Ditunno J., Dobkin B.H., Havton L.A., Ellaway P.H., Fehlings M.G., Privat A., Grossman R., Guest J.D., Kleitman N., Nakamura M., Gaviria M., and Short D. (2007). Guidelines for the conduct of clinical trials for spinal cord injury as developed by the ICCP panel: spontaneous recovery after spinal cord injury and statistical power needed for therapeutic clinical trials. Spinal Cord 45, 190–205 - PubMed
-
- Marino R.J., Barros T., Biering-Sorensen F., Burns S.P., Donovan W.H., Graves D.E., Haak M., Hudson L.M., and Priebe M.M.; ASIA Neurological Standards Committee 2002. (2003). International standards for neurological classification of spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 26, Suppl 1, S50–S56 - PubMed
-
- Waring W.P., 3rd, Biering-Sorensen F., Burns S., Donovan W., Graves D., Jha A., Jones L., Kirshblum S., Marino R., Mulcahey M.J., Reeves R., Scelza W.M., Schmidt-Read M., and Stein A. (2010). 2009 review and revisions of the international standards for the neurological classification of spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 33, 346–352 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bunge R.P., Puckett W.R., and Hiester E.D. (1997). Observations on the pathology of several types of human spinal cord injury, with emphasis on the astrocyte response to penetrating injuries. Adv. Neurol. 72, 305–315 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

