The challenges of introducing routine G6PD testing into radical cure: a workshop report
- PMID: 26416229
- PMCID: PMC4587750
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-015-0896-8
The challenges of introducing routine G6PD testing into radical cure: a workshop report
Abstract
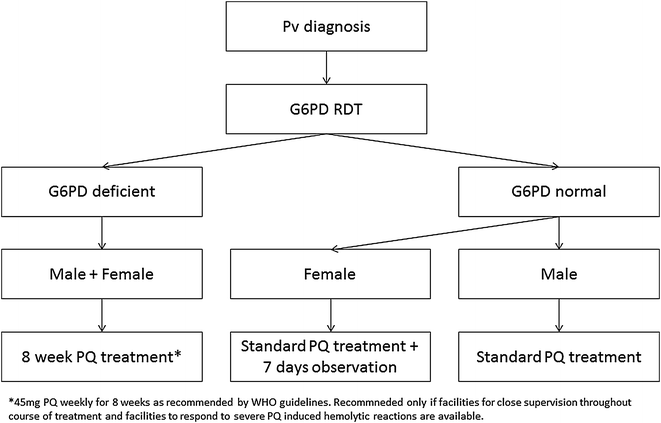
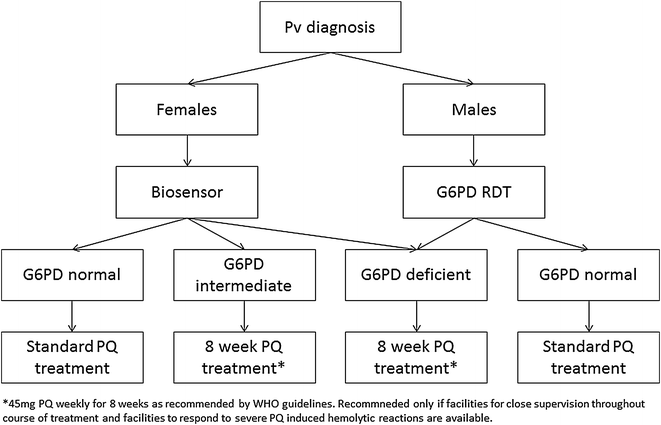
The only currently available drug that effectively removes malaria hypnozoites from the human host is primaquine. The use of 8-aminoquinolines is hampered by haemolytic side effects in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficient individuals. Recently a number of qualitative and a quantitative rapid diagnostic test (RDT) format have been developed that provide an alternative to the current standard G6PD activity assays. The WHO has recently recommended routine testing of G6PD status prior to primaquine radical cure whenever possible. A workshop was held in the Philippines in early 2015 to discuss key challenges and knowledge gaps that hinder the introduction of routine G6PD testing. Two point-of-care (PoC) test formats for the measurement of G6PD activity are currently available: qualitative tests comparable to malaria RDT as well as biosensors that provide a quantitative reading. Qualitative G6PD PoC tests provide a binomial test result, are easy to use and some products are comparable in price to the widely used fluorescent spot test. Qualitative test results can accurately classify hemizygous males, heterozygous females, but may misclassify females with intermediate G6PD activity. Biosensors provide a more complex quantitative readout and are better suited to identify heterozygous females. While associated with higher costs per sample tested biosensors have the potential for broader use in other scenarios where knowledge of G6PD activity is relevant as well. The introduction of routine G6PD testing is associated with additional costs on top of routine treatment that will vary by setting and will need to be assessed prior to test introduction. Reliable G6PD PoC tests have the potential to play an essential role in future malaria elimination programmes, however require an improved understanding on how to best integrate routine G6PD testing into different health settings.
Figures
References
-
- Nasveld PE, Edstein MD, Reid M, Brennan L, Harris IE, Kitchener SJ, et al. Randomized, double-blind study of the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of tafenoquine versus mefloquine for malaria prophylaxis in nonimmune subjects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:792–798. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00354-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous