Exciton dynamics of C60-based single-photon emitters explored by Hanbury Brown-Twiss scanning tunnelling microscopy
- PMID: 26416705
- PMCID: PMC4598842
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9461
Exciton dynamics of C60-based single-photon emitters explored by Hanbury Brown-Twiss scanning tunnelling microscopy
Abstract
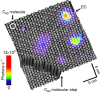
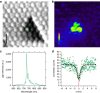
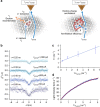
Exciton creation and annihilation by charges are crucial processes for technologies relying on charge-exciton-photon conversion. Improvement of organic light sources or dye-sensitized solar cells requires methods to address exciton dynamics at the molecular scale. Near-field techniques have been instrumental for this purpose; however, characterizing exciton recombination with molecular resolution remained a challenge. Here, we study exciton dynamics by using scanning tunnelling microscopy to inject current with sub-molecular precision and Hanbury Brown-Twiss interferometry to measure photon correlations in the far-field electroluminescence. Controlled injection allows us to generate excitons in solid C60 and let them interact with charges during their lifetime. We demonstrate electrically driven single-photon emission from localized structural defects and determine exciton lifetimes in the picosecond range. Monitoring lifetime shortening and luminescence saturation for increasing carrier injection rates provides access to charge-exciton annihilation dynamics. Our approach introduces a unique way to study single quasi-particle dynamics on the ultimate molecular scale.
Figures

References
-
- Agranovich V. Excitations in Organic Solids Vol. 142 (, OUP Oxford (2009).
-
- Ye Z. et al.. Probing excitonic dark states in single-layer tungsten disulphide. Nature 513, 214–218 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Ugeda M. M. et al.. Giant bandgap renormalization and excitonic effects in a monolayer transition metal dichalcogenide semiconductor. Nat. Mater. 13, 1091–1095 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Reineke S. et al.. White organic light-emitting diodes with fluorescent tube efficiency. Nature 459, 234–238 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Yella A. et al.. Porphyrin-sensitized solar cells with cobalt (II/III)–based redox electrolyte exceed 12 percent efficiency. Science 334, 629–634 (2011). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

