Increased threat of tropical cyclones and coastal flooding to New York City during the anthropogenic era
- PMID: 26417111
- PMCID: PMC4611656
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1513127112
Increased threat of tropical cyclones and coastal flooding to New York City during the anthropogenic era
Abstract
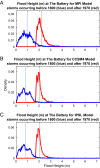
In a changing climate, future inundation of the United States' Atlantic coast will depend on both storm surges during tropical cyclones and the rising relative sea levels on which those surges occur. However, the observational record of tropical cyclones in the North Atlantic basin is too short (A.D. 1851 to present) to accurately assess long-term trends in storm activity. To overcome this limitation, we use proxy sea level records, and downscale three CMIP5 models to generate large synthetic tropical cyclone data sets for the North Atlantic basin; driving climate conditions span from A.D. 850 to A.D. 2005. We compare pre-anthropogenic era (A.D. 850-1800) and anthropogenic era (A.D.1970-2005) storm surge model results for New York City, exposing links between increased rates of sea level rise and storm flood heights. We find that mean flood heights increased by ∼1.24 m (due mainly to sea level rise) from ∼A.D. 850 to the anthropogenic era, a result that is significant at the 99% confidence level. Additionally, changes in tropical cyclone characteristics have led to increases in the extremes of the types of storms that create the largest storm surges for New York City. As a result, flood risk has greatly increased for the region; for example, the 500-y return period for a ∼2.25-m flood height during the pre-anthropogenic era has decreased to ∼24.4 y in the anthropogenic era. Our results indicate the impacts of climate change on coastal inundation, and call for advanced risk management strategies.
Keywords: New Jersey; flood height; relative sea level; storm surge; tropical cyclones.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Emanuel K. Increasing destructiveness of tropical cyclones over the past 30 years. Nature. 2005;436(7051):686–688. - PubMed
-
- Pielke RA., Jr Future economic damage from tropical cyclones: sensitivities to societal and climate changes. Philos Trans R Soc A. 2007;365(1860):2717–2729. - PubMed
-
- Rappaport EN. Fatalities in the United States from Atlantic tropical cyclones: New data and interpretation. Bull Am Meteorol Soc. 2014;95(3):341–346.
-
- Blake ES, Kimberlain TB, Berg RJ, Cangialosi JP, Beven JL., II . Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Sandy (AL182012), 22−29 October 2012. Natl Hurricane Cent; Miami: 2013.
-
- Tebaldi C, Strauss BH, Zervas C. Modelling sea level rise impacts on storm surges along US coasts. Environ Res Lett. 2012;7(1):021001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

