Activation of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 by SEW2871 improves cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease model rats
- PMID: 26417237
- PMCID: PMC4566907
Activation of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 by SEW2871 improves cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease model rats
Abstract
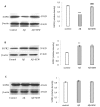
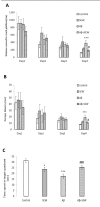
Sphingosine-1 phosphate (S1P) is involved in a variety of cellular processes via activation of S1P receptors (S1PRs; S1PR1 to S1PR5) that are highly expressed in the brain. It has been shown that the level of S1P is reduced in the brain of Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients. However, there is no study designed to evaluate the expression of S1PRs in AD brains. The objectives of the present work are (1) to examine the expression of S1PR1-3 in the hippocampus of beta amyloid (Aβ) 1-42 injected rats and (2) to clarify the effects of chronic S1PR1 activation on S1PR1-3 levels, spatial memory deficit and hippocampal damage in AD rats. SEW2871, the S1PR1 selective agonist, repeatedly was injected intraperitoneally during a period of two weeks. Upon Western Blot data bilateral intrahippocampal injection of Aβ1-42 decreased the expression of S1PR1 while increased S1PR2 level and did not affect that of S1PR3. We found that chronic administration of SEW2871 inhibited the reduction of S1PR1 expression and ameliorated spatial memory impairment in the Morris water maze task in rats. In addition, SEW2871 attenuated the Aβ1-42-induced hippocampal neuronal loss according to Nissl staining findings. Data in the current study highlights the importance of S1PR1 signaling pathway deregulation in AD development and suggests that activation of S1PR1 may represent a potential approach for developing new therapeutics to manage memory deficit and apoptosis associated with neurodegenerative disorders such as AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; SEW2871; cognitive function; sphingosine-1 phosphate receptors.
Figures


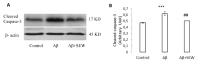
References
-
- Almeida CG, Tampellini D, Takahashi RH, Greengard P, Lin MT, Snyder EM, et al. Beta-amyloid accumulation in APP mutant neurons reduces PSD-95 and GluR1 in synapses. Neurobiol Dis. 2005;20:187–198. - PubMed
-
- Awad AS, Ye H, Huang L, Li L, Foss FW, Jr, Macdonald TL, et al. Selective sphingosine 1-phosphate 1 receptor activation reduces ischemia-reperfusion injury in mouse kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006;290:1516–1524. - PubMed
-
- Bhaskar K, Lamb BT. The role of Aβ and Tau oligomers in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. In: Rahimi F, Bitan G, editors. Non-fibrillar amyloidogenic protein assemblies-common cytotoxins underlying degenerative diseases. New York: Springer; 2012. pp. 135–188.
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
