Human papillomavirus types in non-cervical high-grade intraepithelial neoplasias and invasive carcinomas from San Luis Potosí, Mexico: a retrospective cross-sectional study
- PMID: 26417386
- PMCID: PMC4584459
- DOI: 10.1186/s13027-015-0027-8
Human papillomavirus types in non-cervical high-grade intraepithelial neoplasias and invasive carcinomas from San Luis Potosí, Mexico: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Human papillomavirus types in non-cervical high-grade intraepithelial neoplasias and invasive carcinomas from San Luis Potosí, Mexico: a retrospective cross-sectional study.Infect Agent Cancer. 2016 Feb 25;11:11. doi: 10.1186/s13027-016-0048-y. eCollection 2016. Infect Agent Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26918027 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Viral infections and the burden of high-grade intraepithelial neoplasias (HIN) and invasive carcinomas (IC) associated to infections by human papillomavirus (HPV) types may be prevented by type-specific anti-HPV vaccines. This study determined the prevalence of HPV types in non-cervical HIN and IC diagnosed from 1999 to 2011 at a general hospital in San Luis Potosí, Mexico.
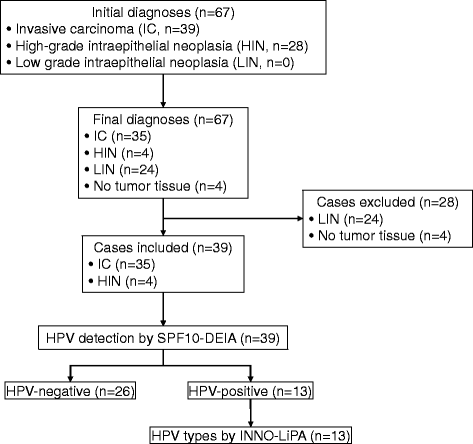
Methods: Review of the 67 formaldehyde-fixed paraffin-embedded non-cervical specimens initially diagnosed as HIN (n = 28) or IC (n = 39) confirmed the presence of tumor tissue in 63 of them and changed the diagnosis of 24 from HIN to low-grade intraepithelial neoplasias, that were excluded from the study. HPV DNA was detected with the SPF10-DNA enzyme immunoassay in the 39 cases included, and viral types in the HPV-positive tumors were identified with the INNO-LiPA linear probe array.
Results: Among the cases included, four HIN were located in the vagina (n = 3) and vulva (n = 1), and 35 IC in the oral cavity (n = 19), penis (n = 8), vagina (n = 7) and vulva (n = 1). There were 13 HPV-positive cases from the vagina (n = 7), vulva (n = 1), penis (n = 1) and oral cavity (n = 1). The viral types identified were the high-risk types HPV16 in the vagina (n = 3) and vulva (n = 3), HPV45 in the vagina (n = 2), HPV59 in the vagina (n = 1) and penis (n = 1), HPV33 in the vagina (n = 1),and HPV35 in the tongue(n = 1); and the low-risk types HPV54 in the vagina (n = 1), and HPV11 in the vulva (n = 1).
Conclusions: Five high-risk viral types (HPV16, 45, 59, 33 and 35) and two low-risk types (HPV11 and 54) infect one third of the non-cervical HIN and IC included. Most infections are by a single HPV high-risk type, the most prevalent one being HPV16. Vagina is the most frequent location of the HPV-positive tumors. Vaccination against HPV16 and HPV18 could have prevented around half of the HPV-positive tumors.
Keywords: HPV; INNO-LiPA; Non-cervical carcinomas; SPF10.
Figures
References
-
- Illades-Aguiar B, Alarcon-Romero Ldel C, Antonio-Vejar V, Zamudio-Lopez N, Sales-Linares N, Flores-Alfaro E, et al. Prevalence and distribution of human papillomavirus types in cervical cancer, squamous intraepithelial lesions, and with no intraepithelial lesions in women from Southern Mexico. Gynecol Oncol. 2010;117(2):291–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2010.01.036. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lizano M, De la Cruz-Hernandez E, Carrillo-Garcia A, Garcia-Carranca A, de Ponce Leon-Rosales S, Duenas-Gonzalez A, et al. Distribution of HPV16 and 18 intratypic variants in normal cytology, intraepithelial lesions, and cervical cancer in a Mexican population. Gynecol Oncol. 2006;102(2):230–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.12.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Montoya-Fuentes H, Suarez Rincon AE, Ramirez-Munoz MP, Arevalo-Lagunas I, Moran Moguel MC, Gallegos Arreola MP, et al. The detection of human papillomavirus 16, 18, 35 and 58 in cervical-uterine cancer and advanced degree of squamous intraepithelial lesions in Western Mexico: clinical-molecular correlation. Ginecol Obstet Mex. 2001;69:137–42. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

