Bedside monitoring of patients with shock using a portable spatially-resolved near-infrared spectroscopy
- PMID: 26417512
- PMCID: PMC4574668
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.6.003431
Bedside monitoring of patients with shock using a portable spatially-resolved near-infrared spectroscopy
Abstract
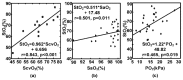
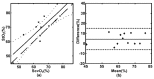
Clinical monitoring of shock mainly depends on blood-oxygen-indices obtained from invasive blood sample tests. The central internal jugular central vein oxygenation level (ScvO2) has been considered as a gold standard indicator for shock prediction. We developed a noninvasive spatially-resolved near-infrared spectroscopy (SR-NIRS) to measure tissue blood oxygen saturation (StO2) surrounding the region of taking blood sample for the ScvO2 test in 25 patients with shock. StO2 values were found to be highly correlated (r = 0.84, p < 0.001) with ScvO2 levels and the concordance coefficient of 0.80 is high. The results suggest the potential of noninvasive SR-NIRS for bedside shock monitoring.
Keywords: (170.1470) Blood or tissue constituent monitoring; (300.0300) Spectroscopy.
Figures


References
-
- Houston M. C., “Pathophysiology of shock,” Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. North Am. 2(2), 143–149 (1990). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
