Atrial fibrillation in heart failure: what should we do?
- PMID: 26419625
- PMCID: PMC4670966
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv513
Atrial fibrillation in heart failure: what should we do?
Abstract
Heart failure (HF) and atrial fibrillation (AF) are two conditions that are likely to dominate the next 50 years of cardiovascular (CV) care. Both are increasingly prevalent and associated with high morbidity, mortality, and healthcare cost. They are closely inter-related with similar risk factors and shared pathophysiology. Patients with concomitant HF and AF suffer from even worse symptoms and poorer prognosis, yet evidence-based evaluation and management of this group of patients is lacking. In this review, we evaluate the common mechanisms for the development of AF in HF patients and vice versa, focusing on the evidence for potential treatment strategies. Recent data have suggested that these patients may respond differently than those with HF or AF alone. These results highlight the clear clinical need to identify and treat according to best evidence, in order to prevent adverse outcomes and reduce the huge burden that HF and AF are expected to have on global healthcare systems in the future. We propose an easy-to-use clinical mnemonic to aid the initial management of newly discovered concomitant HF and AF, the CAN-TREAT HFrEF + AF algorithm (Cardioversion if compromised; Anticoagulation unless contraindication; Normalize fluid balance; Target initial heart rate <110 b.p.m.; Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone modification; Early consideration of rhythm control; Advanced HF therapies; Treatment of other CV disease).
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Heart failure; Management; Review.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


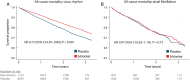
Comment in
-
Letter: Conflicting and unresolved issue of the prognostic value of atrial fibrillation for chronic heart failure patients - Response.Int J Cardiol. 2016 Jul 1;214:516-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.03.107. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Int J Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27087520 No abstract available.
References
-
- Braunwald E. Cardiovascular medicine at the turn of the millennium: triumphs, concerns, and opportunities. N Engl J Med 1997;337:1360–1369. - PubMed
-
- Wodchis WP, Bhatia RS, Leblanc K, Meshkat N, Morra D. A review of the cost of atrial fibrillation. Value Health 2012;15:240–248. - PubMed
-
- Braunschweig F, Cowie MR, Auricchio A. What are the costs of heart failure? Europace 2011;13(Suppl. 2):ii13–ii17. - PubMed
-
- Chugh SS, Havmoeller R, Narayanan K, Singh D, Rienstra M, Benjamin EJ, Gillum RF, Kim YH, McAnulty JH, Jr, Zheng ZJ, Forouzanfar MH, Naghavi M, Mensah GA, Ezzati M, Murray CJ. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation 2014;129:837–847. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

