RALA-mediated delivery of FKBPL nucleic acid therapeutics
- PMID: 26419658
- PMCID: PMC4910961
- DOI: 10.2217/nnm.15.115
RALA-mediated delivery of FKBPL nucleic acid therapeutics
Abstract
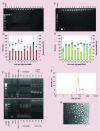
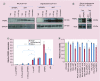
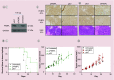
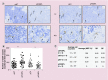
Aims: RALA is a novel 30 mer bioinspired amphipathic peptide that is showing promise for gene delivery. Here, we used RALA to deliver the FK506-binding protein like - FKBPL gene (pFKBPL) - a novel member of the immunophilin protein family. FKBPL is a secreted protein, with overexpression shown to inhibit angiogenesis, tumor growth and stemness, through a variety of intra- and extracellular signaling mechanisms. We also elucidated proangiogenic activity and stemness after utilizing RALA to deliver siRNA (siFKBPL).
Materials & methods: The RALA/pFKBPL and RALA/siFKBPL nanoparticles were characterized in terms of size, charge, stability and toxicity. Overexpression and knockdown of FKBPL was assessed in vitro and in vivo.
Results: RALA delivered both pFKBPL and siFKBPL with less cytotoxicity than commercially available counterparts. In vivo, RALA/pFKBPL delivery retarded tumor growth, and prolonged survival with an associated decrease in angiogenesis, while RALA/siFKBPL had no effect on tumor growth rate or survival, but resulted in an increase in angiogenesis and stemness.
Conclusion: RALA is an effective delivery system for both FKBPL DNA and RNAi and highlights an alternative therapeutic approach to harnessing FKBPL's antiangiogenic and antistemness activity.
Keywords: FKBPL DNA; RALA peptide; RNAi; antiangiogenic; nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
This project was supported through a BBSRC grant awarded to T Robson (BB/I006958/1) covering salary for A Yakkundi. R Bennett was supported by Department of Employment and Learning PhD studentship. NI–MPL is supported by Cancer Research UK, the Experimental Cancer Medicine Centre Network and the Friends of the Cancer Centre. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Rana TM. Illuminating the silence: understanding the structure and function of small RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:23–36. - PubMed
-
- McCrudden CM, McCarthy HO. Bioinspired delivery systems. In: Martin F, editor. Gene Therapy – Tools and Potential Applications. InTech; 2013. ISBN: 978–953–51–1014–9.
-
- McCarthy HO, Zholobenko AV, Wang Y, et al. Evaluation of a multi-functional nanocarrier for targeted breast cancer iNOS gene therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2011;405:196–202. - PubMed
-
- Li W, Nicol F, Szoka FC, Jr, et al. GALA: a designed synthetic pH-responsive amphipathic peptide with applications in drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004;56:967–985. - PubMed
-
• Explains how the amphipathic peptides were designed and function.
-
- Yang J, Liu H, Zhang X. Design, preparation and application of nucleic acid delivery carriers. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014;32(4):804–817. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
