Kidney-specific Sonoporation-mediated Gene Transfer
- PMID: 26419704
- PMCID: PMC4754547
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2015.171
Kidney-specific Sonoporation-mediated Gene Transfer
Abstract
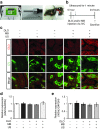
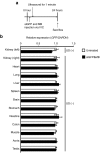
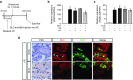
Sonoporation can deliver agents to target local organs by systemic administration, while decreasing the associated risk of adverse effects. Sonoporation has been used for a variety of materials and in a variety of organs. Herein, we demonstrated that local sonoporation to the kidney can offer highly efficient transfer of oligonucleotides, which were systemically administrated to the tubular epithelium with high specificity. Ultrasonic wave irradiation to the kidney collapsed the microbubbles and transiently affected the glomerular filtration barrier and increased glomerular permeability. Oligonucleotides were passed through the barrier all at once and were absorbed throughout the tubular epithelium. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), which plays a central role in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury, was targeted using small interfering RNA (siRNA) with renal sonoporation in a murine model. The reduction of TNFα expression after single gene transfer significantly inhibited the expression of kidney injury markers, suggesting that systemic administration of siRNA under temporary and local sonoporation could be applicable in the clinical setting of ischemic acute kidney injury.
Figures




References
-
- Rewa, O and Bagshaw, SM (2014). Acute kidney injury-epidemiology, outcomes and economics. Nat Rev Nephrol 10: 193–207. - PubMed
-
- Xue, JL, Daniels, F, Star, RA, Kimmel, PL, Eggers, PW, Molitoris, BA et al. (2006). Incidence and mortality of acute renal failure in Medicare beneficiaries, 1992 to 2001. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 1135–1142. - PubMed
-
- Elapavaluru, S and Kellum, JA (2007). Why do patients die of acute kidney injury? Acta Clin Belg Suppl 326–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

