Purification and characterization of tenerplasminin-1, a serine peptidase inhibitor with antiplasmin activity from the coral snake (Micrurus tener tener) venom
- PMID: 26419785
- PMCID: PMC4729579
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.09.009
Purification and characterization of tenerplasminin-1, a serine peptidase inhibitor with antiplasmin activity from the coral snake (Micrurus tener tener) venom
Abstract
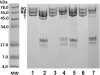
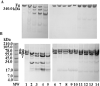
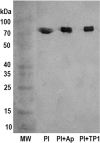
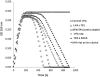
A plasmin inhibitor, named tenerplasminin-1 (TP1), was isolated from Micrurus tener tener (Mtt) venom. It showed a molecular mass of 6542Da, similarly to Kunitz-type serine peptidase inhibitors. The amidolytic activity of plasmin (0.5nM) on synthetic substrate S-2251 was inhibited by 91% following the incubation with TP1 (1nM). Aprotinin (2nM) used as the positive control of inhibition, reduced the plasmin amidolytic activity by 71%. Plasmin fibrinolytic activity (0.05nM) was inhibited by 67% following incubation with TP1 (0.1nM). The degradation of fibrinogen chains induced by plasmin, trypsin or elastase was inhibited by TP1 at a 1:2, 1:4 and 1:20 enzyme:inhibitor ratio, respectively. On the other hand, the proteolytic activity of crude Mtt venom on fibrinogen chains, previously attributed to metallopeptidases, was not abolished by TP1. The tPA-clot lysis assay showed that TP1 (0.2nM) acts like aprotinin (0.4nM) inducing a delay in lysis time and lysis rate which may be associated with the inhibition of plasmin generated from the endogenous plasminogen activation. TP1 is the first serine protease plasmin-like inhibitor isolated from Mtt snake venom which has been characterized in relation to its mechanism of action, formation of a plasmin:TP1 complex and therapeutic potential as anti-fibrinolytic agent, a biological characteristic of great interest in the field of biomedical research. They could be used to regulate the fibrinolytic system in pathologies such as metastatic cancer, parasitic infections, hemophilia and other hemorrhagic syndromes, in which an intense fibrinolytic activity is observed.
Keywords: Fibrinolytic system; Hemostasis; Micrurus tener tener; Plasmin inhibitor; Snake venom.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Aird SD, Da Silva NJ., Jr. Comparative enzymatic composition of Brazilian coral snake (Micrurus) venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B. 1991;99:287–294. - PubMed
-
- Alape-Girón A, Lomonte B, Gustafsson B, Da Silva NJ, Thelestam M. Electrophoretic and immunochemical studies of Micrurus snake venoms. Toxicon. 1994;32:713–723. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee Y, Mizuguchi J, Iwanaga S, Kini M. Hemextin AB complex — a snake venom anticoagulant protein complex that inhibits factor VIIa activity. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2005;34:184–187. - PubMed
-
- Barros ACS, Fernandes DP, Ferreira LCL, Santos MC. Local effects induced by venoms from five species of genus Micrurus sp. coral snakes. Toxicon. 1994;32:445–452. - PubMed
-
- Bode W, Engh R, Musil D, Laber B, Stubbs M, Huber R, Turk V. Mechanism of interaction of cysteine proteinases and their protein inhibitors as compared to the serine proteinase–inhibitor interaction. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler. 1990;371(Suppl.):111–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

