Ammonia Affects Astroglial Proliferation in Culture
- PMID: 26421615
- PMCID: PMC4589356
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139619
Ammonia Affects Astroglial Proliferation in Culture
Abstract
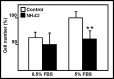
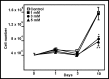
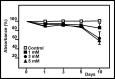
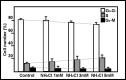
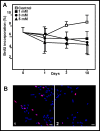
Primary cultures of rat astroglial cells were exposed to 1, 3 and 5 mM NH4Cl for up to 10 days. Dose- and time-dependent reductions in cell numbers were seen, plus an increase in the proportion of cells in the S phase. The DNA content was reduced in the treated cells, and BrdU incorporation diminished. However, neither ammonia nor ammonia plus glutamine had any effect on DNA polymerase activity. iTRAQ analysis showed that exposure to ammonia induced a significant reduction in histone and heterochromatin protein 1 expression. A reduction in cell viability was also noted. The ammonia-induced reduction of proliferative activity in these cultured astroglial cells seems to be due to a delay in the completion of the S phase provoked by the inhibition of chromatin protein synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ammonia induces aquaporin-4 rearrangement in the plasma membrane of cultured astrocytes.Neurochem Int. 2012 Dec;61(8):1314-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2012.09.008. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Neurochem Int. 2012. PMID: 23022607
-
Propofol protects rat astroglial cells against tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced cytotoxicity; the effect on histone and cAMP-response-element-binding protein (CREB) signalling.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009 Dec;60(4):63-9. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 20065498
-
Possible implication of ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) and beta-synuclein in the ammonia effect on cultured rat astroglial cells: a study using DNA and protein microarrays.Neurochem Int. 2006 Jun;48(8):729-38. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2005.12.014. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Neurochem Int. 2006. PMID: 16483693
-
Ammonia-induced miRNA expression changes in cultured rat astrocytes.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 12;6:18493. doi: 10.1038/srep18493. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26755400 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ammonia on ciliary neurotrophic factor mRNA and protein expression and its upstream signalling pathway in cultured rat astroglial cells: possible implication of c-fos, Sp1 and p38MAPK.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2007 Aug;33(4):420-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.2007.00831.x. Epub 2007 Apr 18. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17442060
Cited by
-
Cellular Pathogenesis of Hepatic Encephalopathy: An Update.Biomolecules. 2023 Feb 19;13(2):396. doi: 10.3390/biom13020396. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36830765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xiaochaihutang Improves the Cortical Astrocyte Edema in Thioacetamide-Induced Rat Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy by Activating NRF2 Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Apr 16;11:382. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00382. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32372950 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivity of the Natriuretic Peptide/cGMP System to Hyperammonaemia in Rat C6 Glioma Cells and GPNT Brain Endothelial Cells.Cells. 2021 Feb 15;10(2):398. doi: 10.3390/cells10020398. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33672024 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Nrf2 Transcription Factor and Sp1-Nrf2 Protein Complex in Glutamine Transporter SN1 Regulation in Mouse Cortical Astrocytes Exposed to Ammonia.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 18;22(20):11233. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011233. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681893 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of Transcription Factor Sp1 Promotes SN1 Transporter Regulation by Ammonia in Mouse Cortical Astrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 9;20(2):234. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020234. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30634395 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

