Association of High-Resolution Manometry Metrics with the Symptoms of Achalasia and the Symptomatic Outcomes of Peroral Esophageal Myotomy
- PMID: 26421919
- PMCID: PMC4589231
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139385
Association of High-Resolution Manometry Metrics with the Symptoms of Achalasia and the Symptomatic Outcomes of Peroral Esophageal Myotomy
Abstract
Background: High-resolution manometry (HRM) has improved the accuracy of manometry in detecting achalasia and has helped distinguish between clinically relevant subtypes. This study investigated whether HRM metrics correlate with the achalasia symptoms and symptomatic outcomes of peroral esophageal myotomy (POEM).
Methods: Of the 30 patients who were enrolled, 25 were treated with POEM, 12 of who underwent HRM after 3 months. All the patients completed the Eckardt score questionnaires, and those who underwent POEM were followed up for about 6 months. Pearson correlation was used to assess the relationship between the HRM metrics and symptoms and outcomes.
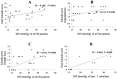
Key results: The integrated relaxation pressure (IRP) score positively correlated with the total Eckardt score, regurgitation score and weight loss score in all the patients, and with the weight loss score in type I achalasia. In 25 patients (10 patients, type I; 15 patients, type II) who underwent POEM, the total Eckardt scores and individual symptom scores significantly decreased after surgery. Changes in the Eckardt scores were similar between type I and type II. Further, the Eckardt scores and weight loss score changes were positively correlated with baseline IRP. Twelve patients (4 patients, type I; 8 patients, type II) underwent HRM again after POEM. IRP changed significantly after POEM, as did the DEP in type II. The IRP changes after POEM were positively correlated with the Eckardt score changes.
Conclusions & inferences: IRP is correlated with the symptoms and outcomes of achalasia patients. Thus, HRM is effective for assessing the severity of achalasia and can predict the efficacy of POEM.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Two-year follow-up for 45 patients with achalasia who underwent peroral endoscopic myotomy.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2015 May;47(5):890-6. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezu320. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2015. PMID: 25193955
-
Function of high-resolution manometry in the analysis of peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia.Surg Endosc. 2016 Mar;30(3):1094-9. doi: 10.1007/s00464-015-4304-9. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Surg Endosc. 2016. PMID: 26099621
-
A clinical study of peroral endoscopic myotomy reveals that impaired lower esophageal sphincter relaxation in achalasia is not only defined by high-resolution manometry.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 2;13(4):e0195423. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195423. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29608597 Free PMC article.
-
Perspective on peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia: Zhongshan experience.Gut Liver. 2015 Mar;9(2):152-8. doi: 10.5009/gnl14227. Gut Liver. 2015. PMID: 25721002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update in achalasia: what the surgeon needs to know.ANZ J Surg. 2016 Jul;86(7-8):555-9. doi: 10.1111/ans.13497. Epub 2016 Mar 18. ANZ J Surg. 2016. PMID: 26992650 Review.
Cited by
-
Characteristics of Achalasia Subtypes: Result of a Study in a Tertiary Hospital.Caspian J Intern Med. 2022 Winter;13(1):100-106. doi: 10.22088/cjim.13.1.100. Caspian J Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35178214 Free PMC article.
-
Peroral endoscopic myotomy compared to laparoscopic Heller myotomy and pneumatic dilation in the treatment of achalasia: a systematic review.Dis Esophagus. 2024 Jan 1;37(1):doad055. doi: 10.1093/dote/doad055. Dis Esophagus. 2024. PMID: 37539633 Free PMC article.
-
Intraoperative use of a functional lumen imaging probe during peroral endoscopic myotomy in patients with achalasia: A single-institute experience and systematic review.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 9;15(6):e0234295. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234295. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32516319 Free PMC article.
-
Updated Systematic Review of Achalasia, with a Focus on POEM Therapy.Dig Dis Sci. 2020 Jan;65(1):38-65. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05784-3. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Dig Dis Sci. 2020. PMID: 31451984
-
Automatic three-dimensional reconstruction of the oesophagus in achalasia patients undergoing POEM: an innovative approach for evaluating treatment outcomes.BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2024 Jun 6;11(1):e001396. doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2024-001396. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38844375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eckardt VF. Clinical presentations and complications of achalasia. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2001; 11(2):281–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

