Novel Vitamin D Receptor Mutations in Hereditary Vitamin D Resistant Rickets in Chinese
- PMID: 26422470
- PMCID: PMC4589239
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138152
Novel Vitamin D Receptor Mutations in Hereditary Vitamin D Resistant Rickets in Chinese
Abstract
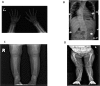
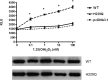
Hereditary 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D-resistant rickets (HVDRR), a rare recessive disease, is caused by mutation in the VDR gene encoding the vitamin D receptor leading to the resistance to vitamin D. We described a female toddler with initial presentation of leg tenderness and clinical features of HVDRR including severe rickets, hypocalcemia and hypophosphatemia without alopecia. Genetic analysis revealed novel compound heterozygous mutations of p.M4I and p.H229Q in patient's VDR gene. In cis p.M4I with FOKI-F eliminated both translation start sites of the VDR protein. The p.H229Q VDR exhibited significantly reduced VDR transactivation activity with intact dimerization with RXR. Our report expanded the mutation spectrum of HVDRR, and provided the first case of a benign variant p.M4I plus a common p.M1T polymorphism leading to a pathogenic allele.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hereditary 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-resistant rickets with alopecia resulting from a novel missense mutation in the DNA-binding domain of the vitamin D receptor.Mol Genet Metab. 2010 Jan;99(1):72-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.09.004. Mol Genet Metab. 2010. PMID: 19815438 Free PMC article.
-
Hereditary 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D resistant rickets due to a mutation causing multiple defects in vitamin D receptor function.Endocrinology. 2004 Nov;145(11):5106-14. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-0080. Epub 2004 Aug 12. Endocrinology. 2004. PMID: 15308610
-
Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms in hypocalcemic vitamin D-resistant rickets carriers.Horm Res. 2007;67(4):179-83. doi: 10.1159/000097014. Epub 2006 Nov 13. Horm Res. 2007. PMID: 17106204
-
The vitamin D hormone and its nuclear receptor: molecular actions and disease states.J Endocrinol. 1997 Sep;154 Suppl:S57-73. J Endocrinol. 1997. PMID: 9379138 Review.
-
Lessons Learned from Hereditary 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D-Resistant Rickets Patients on Vitamin D Functions.J Nutr. 2021 Mar 11;151(3):473-481. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxaa380. J Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33438017 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Vitamin D Receptor Genotypes on Taiwan Hallux Valgus.In Vivo. 2024 Jul-Aug;38(4):1601-1608. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13610. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 38936889 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Stat3 signaling ameliorates atrophy of the soleus muscles in mice lacking the vitamin D receptor.Skelet Muscle. 2017 Jan 25;7(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13395-017-0121-2. Skelet Muscle. 2017. PMID: 28122601 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tiosano D, Wildbaum G, Gepstein V, Verbitsky O, Weisman Y, Karin N, et al. The role of vitamin D receptor in innate and adaptive immunity: a study in hereditary vitamin D-resistant rickets patients. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism. 2013;98(4):1685–93. Epub 2013/03/14. 10.1210/jc.2012-3858 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

