Detailed classification of swimming paths in the Morris Water Maze: multiple strategies within one trial
- PMID: 26423140
- PMCID: PMC4589698
- DOI: 10.1038/srep14562
Detailed classification of swimming paths in the Morris Water Maze: multiple strategies within one trial
Abstract
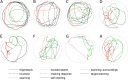
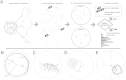
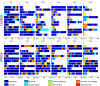
The Morris Water Maze is a widely used task in studies of spatial learning with rodents. Classical performance measures of animals in the Morris Water Maze include the escape latency, and the cumulative distance to the platform. Other methods focus on classifying trajectory patterns to stereotypical classes representing different animal strategies. However, these approaches typically consider trajectories as a whole, and as a consequence they assign one full trajectory to one class, whereas animals often switch between these strategies, and their corresponding classes, within a single trial. To this end, we take a different approach: we look for segments of diverse animal behaviour within one trial and employ a semi-automated classification method for identifying the various strategies exhibited by the animals within a trial. Our method allows us to reveal significant and systematic differences in the exploration strategies of two animal groups (stressed, non-stressed), that would be unobserved by earlier methods.
Figures
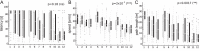
References
-
- Morris R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 11, 47–60 (1984). - PubMed
-
- Morris R. Spatial localization does not require the presence of local cues. Learn. Motiv. 260, 239–260 (1981).
-
- D’Hooge R. & Deyn P. D. Applications of the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Res. Rev. 36, 60–90 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Brandeis R., Brandys Y. & Yehuda S. The use of the morris water maze in the study of memory and learning. Int. J. Neurosci. 48, 29–69 (1989). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

