The epidemiology of subclinical malaria infections in South-East Asia: findings from cross-sectional surveys in Thailand-Myanmar border areas, Cambodia, and Vietnam
- PMID: 26424000
- PMCID: PMC4590703
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-015-0906-x
The epidemiology of subclinical malaria infections in South-East Asia: findings from cross-sectional surveys in Thailand-Myanmar border areas, Cambodia, and Vietnam
Abstract
Background: The importance of the submicroscopic reservoir of Plasmodium infections for malaria elimination depends on its size, which is generally considered small in low transmission settings. The precise estimation of this reservoir requires more sensitive parasite detection methods. The prevalence of asymptomatic, sub-microscopic malaria was assessed by a sensitive, high blood volume quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction method in three countries of the Greater Mekong Sub-region.
Methods: Cross-sectional surveys were conducted in three villages in western Cambodia, four villages along the Thailand-Myanmar border and four villages in southwest Vietnam. Malaria parasitaemia was assessed by Plasmodium falciparum/pan malaria rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs), microscopy and a high volume ultra-sensitive real-time polymerase chain reaction (HVUSqPCR: limit of detection 22 parasites/mL). All villagers older than 6 months were invited to participate.
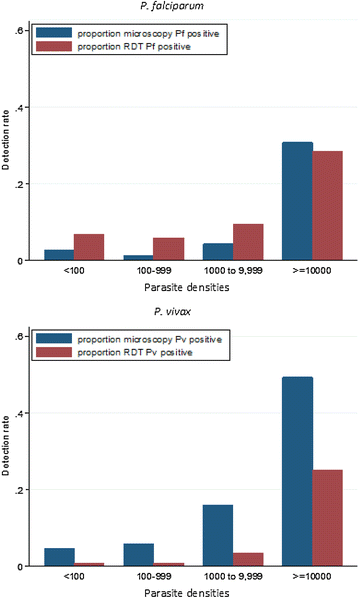
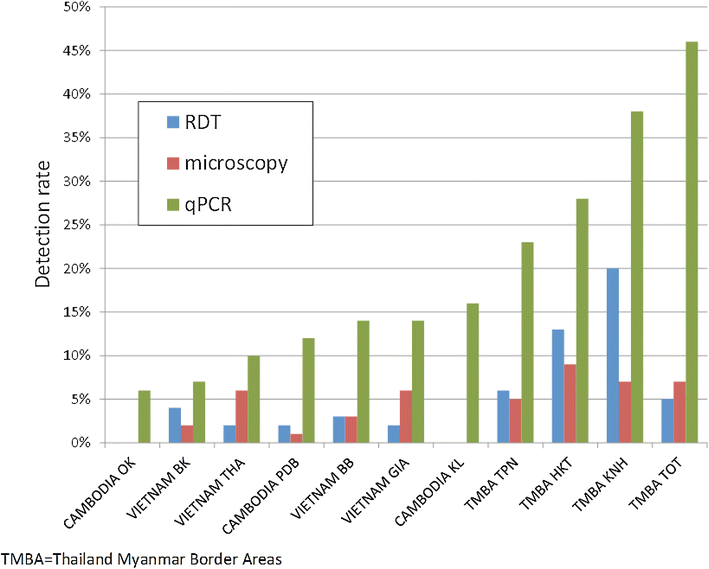
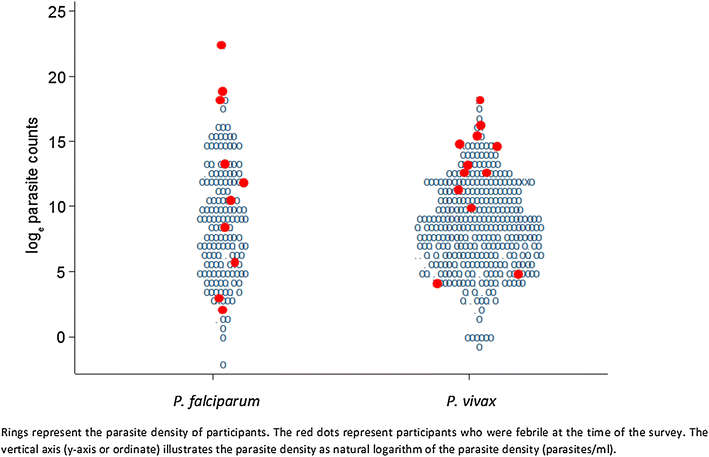
Results: A census before the surveys identified 7355 residents in the study villages. Parasite prevalence was 224/5008 (4 %) by RDT, 229/5111 (5 %) by microscopy, and 988/4975 (20 %) when assessed by HVUSqPCR. Of these 164 (3 %) were infected with P. falciparum, 357 (7 %) with Plasmodium vivax, 56 (1 %) with a mixed infection, and 411 (8 %) had parasite densities that were too low for species identification. A history of fever, male sex, and age of 15 years or older were independently associated with parasitaemia in a multivariate regression model stratified by site.
Conclusion: Light microscopy and RDTs identified only a quarter of all parasitaemic participants. The asymptomatic Plasmodium reservoir is considerable, even in low transmission settings. Novel strategies are needed to eliminate this previously under recognized reservoir of malaria transmission.
Figures


References
-
- Wongsrichanalai C, Barcus MJ, Muth S, Sutamihardja A, Wernsdorfer WH. A review of malaria diagnostic tools: microscopy and rapid diagnostic test (RDT) Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007;77:119–127. - PubMed
-
- Snounou G, Viriyakosol S, Zhu XP, Jarra W, Pinheiro L, do Rosario VE, et al. High sensitivity of detection of human malaria parasites by the use of nested polymerase chain reaction. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993;61:315–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

