Erysipelas, a large retrospective study of aetiology and clinical presentation
- PMID: 26424182
- PMCID: PMC4590694
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-015-1134-2
Erysipelas, a large retrospective study of aetiology and clinical presentation
Abstract
Background: Erysipelas is a common and severe infection where the aetiology and optimal management is not well-studied. Here, we investigate the clinical features, bacteriological aetiology, and treatment of erysipelas.
Methods: Episodes of erysipelas in a seven-years period in our institution were studied retrospectively using a pre-specified protocol and is presented with descriptive and comparative statistics.
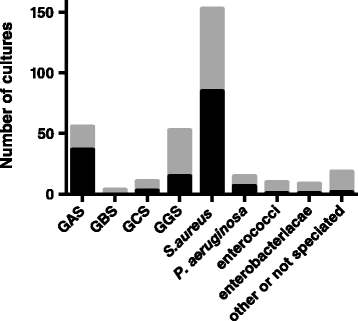
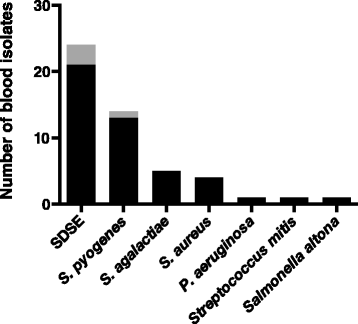
Results: 1142 episodes of erysipelas were identified in 981 patients. Patients had a median age of 61 years, 59 % were male, a majority had underlying diseases or predisposing conditions, and the leg was most often affected. Wound cultures were taken in 343 episodes and 56 grew group A streptococci (GAS), 53 grew group G streptococci (GGS), 11 grew group C streptococci (GCS), and 153 grew Staphylococcus aureus. Blood cultures were drawn in 49 % of episodes and 50 cultures were positive with GGS as the most common finding (21 cultures) followed by GAS in 13, group B streptococci in 5, S. aureus in 4, and GCS in 3 cultures. In 45 % of episodes, patients received antibiotics with activity against S. aureus.
Conclusions: GGS is the most common streptococcus isolated in erysipelas and the role of S. aureus in erysipelas remains elusive.
Figures
References
-
- Goettsch WG, Bouwes Bavinck JN, Herings RMC. Burden of illness of bacterial cellulitis and erysipelas of the leg in the Netherlands. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:834–9. - PubMed
-
- Stevens DL, Bisno AL, Chambers HF, Dellinger EP, Goldstein EJC, Gorbach SL, et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft tissue infections: 2014 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:e10–52. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu296. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

