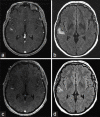
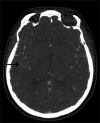
A completely thrombosed, nongiant middle cerebral artery aneurysm mimicking an intra-axial neoplasm
- PMID: 26425396
- PMCID: PMC4571614
- DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.164696
A completely thrombosed, nongiant middle cerebral artery aneurysm mimicking an intra-axial neoplasm
Abstract
Background: Few reports exist regarding thrombosed aneurysms where the initial work up was concerning for a neoplasm. To date, no published reports exist regarding a nongiant thrombosed middle cerebral artery aneurysm, where the primary workup and treatment plan was directed toward a preliminary diagnosis of intra-axial neoplasm.
Case description: We report a 43-year-old female who presented with a generalized tonic-clonic seizure attributed to a lesion along the right superior temporal gyrus. The lesion enhanced on initial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain, as well as on follow-up MRI. Subsequent vascular studies and metastatic work up were negative. A craniotomy with image guidance was performed and an intraoperative diagnosis was made of a thrombosed aneurysm along a branch of the middle cerebral artery. The aneurysm was trapped and resected as there was no significant flow from the branch as seen on the prior cerebral angiogram. The patient had an uneventful postoperative course.
Conclusion: Completely thrombosed, nongiant aneurysms can mimic an intra-axial neoplasm. Typical imaging features for thrombosed aneurysms may be missed, especially if the aneurysms are small, where imaging characteristics of the intraluminal contents is more difficult to appreciate. Although imaging may be consistent with a neoplastic lesion, there should be suspicion for a potential underlying aneurysm.
Keywords: Complete thrombosis; middle cerebral artery; neoplasm; seizures; thrombosed cerebral aneurysm.
Figures
References
-
- Bakker NA, Groen RJ, Foumani M, Uyttenboogaart M, Eshghi OS, Metzemaekers JD, et al. Repeat digital subtraction angiography after a negative baseline assessment in nonperimesencephalic subarachnoid hemorrhage: A pooled data meta-analysis. J Neurosurg. 2014;120:99–103. - PubMed
-
- Calviere L, Viguier A, Da Silva NA, Jr, Cognard C, Larrue V. Unruptured intracranial aneurysm as a cause of cerebral ischemia. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2011;113:28–33. - PubMed
-
- da Rocha AJ, da Silva CJ, Gama HP, Baccin CE, Braga FT, Cesare Fde A, Veiga JC. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging sequences with computed tomography to detect low-grade subarachnoid hemorrhage: Role of fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequence. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2006;30:295–303. - PubMed
-
- Dashti R, Rinne J, Hernesniemi J, Niemelä M, Kivipelto L, Lehecka M, et al. Microneurosurgical management of proximal middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Surg Neurol. 2007;67:6–14. - PubMed
-
- De Luca GP, Volpin L, Colombo F, Fornezza U, Pinna V. Spontaneous healing of cerebral aneurysm at the beginning of left posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA). Case report. J Neurosurg Sci. 1998;42:115–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources