Trousseau's Syndrome, a Previously Unrecognized Condition in Acute Ischemic Stroke Associated With Myocardial Injury
- PMID: 26425612
- PMCID: PMC4528894
- DOI: 10.1177/2324709614539283
Trousseau's Syndrome, a Previously Unrecognized Condition in Acute Ischemic Stroke Associated With Myocardial Injury
Abstract
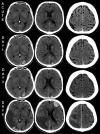
Trousseau's syndrome is a well-known malignancy associated hypercoagulative state leading to venous or arterial thrombosis. The pathophysiology is however poorly understood, although multiple mechanisms are believed to be involved. We report a case of Trousseau's syndrome resulting in concomitant cerebral and myocardial microthrombosis, presenting with acute ischemic stroke and markedly elevated plasma troponin T levels suggesting myocardial injury. Without any previous medical history, the patient developed multiple cerebral infarctions and died within 11 days of admission. The patient was postmortem diagnosed with an advanced metastatic adenocarcinoma of the prostate with disseminated cerebral, pulmonary, and myocardial microthrombosis. Further analyses revealed, to the best of our knowledge for the first time in stroke patients, circulating microvesicles positive for the epithelial tumor marker CK18 and citrullinated histone H3 in thrombi, markers of the recently described cancer-associated procoagulant DNA-based neutrophil extracellular traps. We also found tissue factor, the main in vivo initiator of coagulation, both in thrombi and in metastases. Troponin elevation in acute ischemic stroke is common and has repeatedly been associated with an increased risk of mortality. The underlying pathophysiology is however not fully clarified, although a number of possible explanations have been proposed. We now suggest that unexplainable high levels of troponin in acute ischemic stroke deserve special attention in terms of possible occult malignancy.
Keywords: Trousseau; malignancy; myocardial infarction; stroke; thrombosis; troponin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Trousseau A. Phlegmasia alba dolens. Lectures on Clinical Medicine, Delivered at the Hotel-Dieu, Paris. Vol. 5 London, England: New Sydenham Society; 1865:281-332.
-
- Davila M, Amirkhosravi A, Coll E, et al. Tissue factor-bearing microparticles derived from tumor cells: impact on coagulation activation. J Thromb Haemost. 2008;6:1517-1524. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

