Gene Signatures Stratify Computed Tomography Screening Detected Lung Cancer in High-Risk Populations
- PMID: 26425689
- PMCID: PMC4563137
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.07.001
Gene Signatures Stratify Computed Tomography Screening Detected Lung Cancer in High-Risk Populations
Abstract
Background: Although screening programmes of smokers have detected resectable early lung cancers more frequently than expected, their efficacy in reducing mortality remains debatable. To elucidate the biological features of computed tomography (CT) screening detected lung cancer, we examined the mRNA signatures on tumours according to the year of detection, stage and survival.
Methods: Gene expression profiles were analysed on 28 patients (INT-IEO training cohort) and 24 patients of Multicentre Italian Lung Detection (MILD validation cohort). The gene signatures generated from the training set were validated on the MILD set and a public deposited DNA microarray data set (GSE11969). Expression of selected genes and proteins was validated by real-time RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry. Enriched core pathway and pathway networks were explored by GeneSpring GX10.
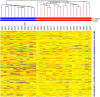
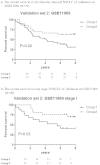
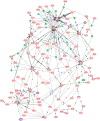
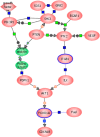
Findings: A 239-gene signature was identified according to the year of tumour detection in the training INT-IEO set and correlated with the patients' outcomes. These signatures divided the MILD patients into two distinct survival groups independently of tumour stage, size, histopathological type and screening year. The signatures can also predict survival in the clinically detected cancers (GSE11969). Pathway analyses revealed tumours detected in later years enrichment of the PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathway, with up-regulation of PDPK1, ITGB1 and down-regulation of FOXO1A. Analysis of normal lung tissue from INT-IEO cohort produced signatures distinguishing patients with early from late detected tumours.
Interpretation: The distinct pattern of "indolent" and "aggressive" tumour exists in CT-screening detected lung cancer according to the gene expression profiles. The early development of an aggressive phenotype may account for the lack of mortality reduction by screening observed in some cohorts.
Keywords: Aggressive; CT screening; Gene signature; Indolent; Lung cancer; PI3K/PTEN/AKT signalling pathway.
Figures


References
-
- Akiyama S.K., Olden K., Yamada K.M. Fibronectin and integrins in invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1995;14(3):173–189. (Epub 1995/09/01) - PubMed
-
- Anon. Screening for lung cancer. Too many uncertainties, even for smokers. Prescrire Int. 2014;23(145):19–23. (Jan) - PubMed
-
- Bach P.B. Is our natural-history model of lung cancer wrong? Lancet Oncol. 2008;9(7):693–697. (Epub 2008/07/05) - PubMed
-
- Bach P.B., Kelley M.J., Tate R.C., McCrory D.C. Screening for lung cancer: a review of the current literature. Chest. 2003;123(1 Suppl.):72S–82S. - PubMed
-
- Balsara B.R., Pei J., Mitsuuchi Y. Frequent activation of AKT in non-small cell lung carcinomas and preneoplastic bronchial lesions. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25(11):2053–2059. (Epub 2004/07/09) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

