Histone Modifications, Modifiers and Readers in Melanoma Resistance to Targeted and Immune Therapy
- PMID: 26426052
- PMCID: PMC4695870
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers7040870
Histone Modifications, Modifiers and Readers in Melanoma Resistance to Targeted and Immune Therapy
Abstract
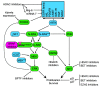
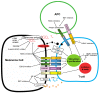
The treatment of melanoma has been revolutionized by new therapies targeting MAPK signaling or the immune system. Unfortunately these therapies are hindered by either primary resistance or the development of acquired resistance. Resistance mechanisms involving somatic mutations in genes associated with resistance have been identified in some cases of melanoma, however, the cause of resistance remains largely unexplained in other cases. The importance of epigenetic factors targeting histones and histone modifiers in driving the behavior of melanoma is only starting to be unraveled and provides significant opportunity to combat the problems of therapy resistance. There is also an increasing ability to target these epigenetic changes with new drugs that inhibit these modifications to either prevent or overcome resistance to both MAPK inhibitors and immunotherapy. This review focuses on changes in histones, histone reader proteins and histone positioning, which can mediate resistance to new therapeutics and that can be targeted for future therapies.
Keywords: BET; BRAF; EZH2; HDAC; MEK; PD-1; PD-L1; PRC2; RAF; bromodomain; chromatin modifiers; histones; immunotherapy; methyltransferase; resistance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors to Overcome Resistance to Targeted and Immuno Therapy in Metastatic Melanoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 17;8:486. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00486. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32626712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Future perspectives in melanoma research: meeting report from the "Melanoma Bridge": Napoli, December 3rd-6th 2014.J Transl Med. 2015 Nov 30;13:374. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0736-1. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26619946 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Therapeutic Approaches for Melanoma Patients Targeting Epigenetic Modifiers.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 8;13(24):6180. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246180. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The activation of MAPK in melanoma cells resistant to BRAF inhibition promotes PD-L1 expression that is reversible by MEK and PI3K inhibition.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Feb 1;19(3):598-609. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2731. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23095323
-
The Histone Methyltransferase Ezh2 Controls Mechanisms of Adaptive Resistance to Tumor Immunotherapy.Cell Rep. 2017 Jul 25;20(4):854-867. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.07.007. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28746871
Cited by
-
N-Acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase (Arylsulfatase B) Regulates PD-L1 Expression in Melanoma by an HDAC3-Mediated Epigenetic Mechanism.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 28;25(11):5851. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115851. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892038 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of coexistence of BRAF V600E mutation and EZH2 gain specifically in melanoma as a promising target for combination therapy.J Transl Med. 2017 Dec 4;15(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1344-z. J Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 29202777 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Therapies in Melanoma-Targeting DNA Methylation and Histone Modification.Biomedicines. 2025 May 13;13(5):1188. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051188. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40427015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
4SC-202 exerts an anti-tumor effect in cervical cancer by targeting PRLR signaling pathway.J Mol Histol. 2022 Dec;53(6):891-902. doi: 10.1007/s10735-022-10105-6. Epub 2022 Oct 22. J Mol Histol. 2022. PMID: 36272045
-
Novel HSP90-PI3K Dual Inhibitor Suppresses Melanoma Cell Proliferation by Interfering with HSP90-EGFR Interaction and Downstream Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 7;21(5):1845. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051845. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32156008 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

