Non-Conserved Residues in Clostridium acetobutylicum tRNA(Ala) Contribute to tRNA Tuning for Efficient Antitermination of the alaS T Box Riboswitch
- PMID: 26426057
- PMCID: PMC4695836
- DOI: 10.3390/life5041567
Non-Conserved Residues in Clostridium acetobutylicum tRNA(Ala) Contribute to tRNA Tuning for Efficient Antitermination of the alaS T Box Riboswitch
Abstract
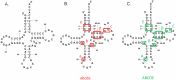
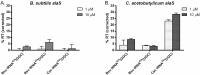
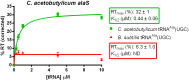
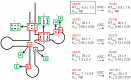
The T box riboswitch regulates expression of amino acid-related genes in Gram-positive bacteria by monitoring the aminoacylation status of a specific tRNA, the binding of which affects the folding of the riboswitch into mutually exclusive terminator or antiterminator structures. Two main pairing interactions between the tRNA and the leader RNA have been demonstrated to be necessary, but not sufficient, for efficient antitermination. In this study, we used the Clostridium acetobutylicum alaS gene, which encodes alanyl-tRNA synthetase, to investigate the specificity of the tRNA response. We show that the homologous C. acetobutylicum tRNA(Ala) directs antitermination of the C. acetobutylicum alaS gene in vitro, but the heterologous Bacillus subtilis tRNA(Ala) (with the same anticodon and acceptor end) does not. Base substitutions at positions that vary between these two tRNAs revealed synergistic and antagonistic effects. Variation occurs primarily at positions that are not conserved in tRNA(Ala) species, which indicates that these non-conserved residues contribute to optimal antitermination of the homologous alaS gene. This study suggests that elements in tRNA(Ala) may have coevolved with the homologous alaS T box leader RNA for efficient antitermination.
Keywords: T box; antitermination; riboswitch; tRNA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The T-Box Riboswitch: tRNA as an Effector to Modulate Gene Regulation.Microbiol Spectr. 2018 Jul;6(4):10.1128/microbiolspec.rwr-0028-2018. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.RWR-0028-2018. Microbiol Spectr. 2018. PMID: 30051797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Codon-Anticodon Recognition in the Bacillus subtilis glyQS T Box Riboswitch: RNA-DEPENDENT CODON SELECTION OUTSIDE THE RIBOSOME.J Biol Chem. 2015 Sep 18;290(38):23336-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.673236. Epub 2015 Jul 30. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26229106 Free PMC article.
-
Two-codon T-box riboswitch binding two tRNAs.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jul 30;110(31):12756-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1304307110. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23858450 Free PMC article.
-
tRNA determinants for transcription antitermination of the Bacillus subtilis tyrS gene.RNA. 2000 Aug;6(8):1131-41. doi: 10.1017/s1355838200992100. RNA. 2000. PMID: 10943892 Free PMC article.
-
An evolving tale of two interacting RNAs-themes and variations of the T-box riboswitch mechanism.IUBMB Life. 2019 Aug;71(8):1167-1180. doi: 10.1002/iub.2098. Epub 2019 Jun 17. IUBMB Life. 2019. PMID: 31206978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The T-Box Riboswitch: tRNA as an Effector to Modulate Gene Regulation.Microbiol Spectr. 2018 Jul;6(4):10.1128/microbiolspec.rwr-0028-2018. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.RWR-0028-2018. Microbiol Spectr. 2018. PMID: 30051797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A riboswitch gives rise to multi-generational phenotypic heterogeneity in an auxotrophic bacterium.Nat Commun. 2020 Mar 5;11(1):1203. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15017-1. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32139702 Free PMC article.
-
Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases in the Bacterial World.EcoSal Plus. 2016 May;7(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0002-2016. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0002-2016. EcoSal Plus. 2016. PMID: 27223819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Capture and Release of tRNA by the T-Loop Receptor in the Function of the T-Box Riboswitch.Biochemistry. 2017 Jul 18;56(28):3549-3558. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00284. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Biochemistry. 2017. PMID: 28621923 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

