The Effect of the Nonlinearity of the Response of Lipid Membranes to Voltage Perturbations on the Interpretation of Their Electrical Properties. A New Theoretical Description
- PMID: 26426061
- PMCID: PMC4703996
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes5040495
The Effect of the Nonlinearity of the Response of Lipid Membranes to Voltage Perturbations on the Interpretation of Their Electrical Properties. A New Theoretical Description
Abstract
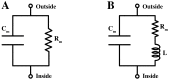
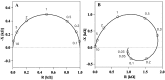
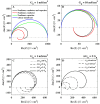
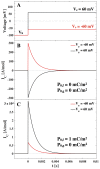
Our understanding of the electrical properties of cell membranes is derived from experiments where the membrane is exposed to a perturbation (in the form of a time-dependent voltage or current change) and information is extracted from the measured output. The interpretation of such electrical recordings consists in finding an electronic equivalent that would show the same or similar response as the biological system. In general, however, there is no unique circuit configuration, which can explain a single electrical recording and the choice of an electric model for a biological system is based on complementary information (most commonly structural information) of the system investigated. Most of the electrophysiological data on cell membranes address the functional role of protein channels while assuming that the lipid matrix is an insulator with constant capacitance. However, close to their melting transition the lipid bilayers are no inert insulators. Their conductivity and their capacitance are nonlinear functions of both voltage, area and volume density. This has to be considered when interpreting electrical data. Here we show how electric data commonly interpreted as gating currents of proteins and inductance can be explained by the nonlinear dynamics of the lipid matrix itself.
Keywords: capacitance; conduction; electrophysiology; impedance; inductance; lipid membrane.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-linear Conductance, Rectification, and Mechanosensitive Channel Formation of Lipid Membranes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 26;8:592520. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.592520. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33575253 Free PMC article.
-
Specific electrical capacitance and voltage breakdown as a function of temperature for different planar lipid bilayers.Bioelectrochemistry. 2016 Dec;112:132-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2016.02.009. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Bioelectrochemistry. 2016. PMID: 26948707
-
Evidence for nonlinear capacitance in biomembrane channel system.J Theor Biol. 1999 Oct 7;200(3):299-305. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.1999.0993. J Theor Biol. 1999. PMID: 10527719
-
Molecular aspects of electrical excitation in lipid bilayers and cell membranes.Horiz Biochem Biophys. 1976;2:230-84. Horiz Biochem Biophys. 1976. PMID: 776770 Review.
-
Lipid ion channels.Biophys Chem. 2010 Aug;150(1-3):2-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2010.02.018. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Biophys Chem. 2010. PMID: 20385440 Review.
Cited by
-
Water Pores in Planar Lipid Bilayers at Fast and Slow Rise of Transmembrane Voltage.Membranes (Basel). 2021 Apr 5;11(4):263. doi: 10.3390/membranes11040263. Membranes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33916447 Free PMC article.
-
Real-Time Impedance Detection of Intra-Articular Space in a Porcine Model Using a Monopolar Injection Needle.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Aug 17;20(16):4625. doi: 10.3390/s20164625. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32824575 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of Hydroxide Ion Conductivity Measurement for Alkaline Water Electrolysis Membranes.Membranes (Basel). 2022 May 26;12(6):556. doi: 10.3390/membranes12060556. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35736263 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of the subthreshold oscillation induced by the neurons' resonance upon the electrical stimulation-dependent instability.Front Neurosci. 2023 May 9;17:1178606. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1178606. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37229430 Free PMC article.
-
Non-linear Conductance, Rectification, and Mechanosensitive Channel Formation of Lipid Membranes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 26;8:592520. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.592520. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33575253 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

