Cell-Based Assay Design for High-Content Screening of Drug Candidates
- PMID: 26428732
- PMCID: PMC5906801
- DOI: 10.4014/jmb.1508.08007
Cell-Based Assay Design for High-Content Screening of Drug Candidates
Abstract
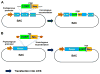
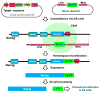
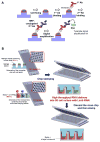
To reduce attrition in drug development, it is crucial to consider the development and implementation of translational phenotypic assays as well as decipher diverse molecular mechanisms of action for new molecular entities. High-throughput fluorescence and confocal microscopes with advanced analysis software have simplified the simultaneous identification and quantification of various cellular processes through what is now referred to as highcontent screening (HCS). HCS permits automated identification of modifiers of accessible and biologically relevant targets and can thus be used to detect gene interactions or identify toxic pathways of drug candidates to improve drug discovery and development processes. In this review, we summarize several HCS-compatible, biochemical, and molecular biology-driven assays, including immunohistochemistry, RNAi, reporter gene assay, CRISPR-Cas9 system, and protein-protein interactions to assess a variety of cellular processes, including proliferation, morphological changes, protein expression, localization, post-translational modifications, and protein-protein interactions. These cell-based assay methods can be applied to not only 2D cell culture but also 3D cell culture systems in a high-throughput manner.
Keywords: 3D cell culture system; Cell-based Assay; Drug discovery; High content screening.
Figures

References
-
- Arkin MR, Glicksman MA, Fu H, Havel JJ, Du Y. Inhibition of protein-protein interactions: non-cellular assay formats. In: Sittampalam GS, Coussens NP, Nelson H, Arkin M, Auld D, Austin C, et al., editors. Assay Guidance Manual. Bethesda, MD: 2004. - PubMed
-
- Arkin MR, Wells JA. Small-molecule inhibitors of protein-protein interactions: progressing towards the dream. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:301–317. - PubMed
-
- Arnone MI, Dmochowski IJ, Gache C. Using reporter genes to study cis-regulatory elements. Methods Cell Biol. 2004;74:621–652. - PubMed
-
- Ashburn TT, Thor KB. Drug repositioning: identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:673–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

