Protective Effects of UCF-101 on Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion (CIR) is Depended on the MAPK/p38/ERK Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 26429193
- PMCID: PMC11482449
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-015-0275-6
Protective Effects of UCF-101 on Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion (CIR) is Depended on the MAPK/p38/ERK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
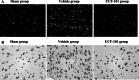
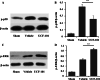
This study was aimed to investigate the treatment mechanisms of 5-[5-(2-nitrophenyl) furfuryliodine]-1,3-diphenyl-2-thiobarbituric acid (UCF-101) in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (CIR) model rats. Total of 54 healthy male Wistar rats were randomly assigned into three groups, namely sham group, vehicle group, and UCF-101 group. The CIR-injured model was established by right middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion. Neurological function was assessed by an investigator according to the Longa neurologic deficit scores. Meanwhile, the cerebral tissue morphology and apoptotic neurons were evaluated by H&E and TUNEL staining, respectively. Additionally, the expressions of caspase 3, p-p38, and p-ERK were detected by immunohistochemistry or/and Western blotting assays. As results, neurologic deficit and pathological damage were obviously enhanced and TUNEL positive neurons were significantly increased in CIR-injured rats, as compared with those in sham group. Furthermore, the expressions of caspase 3, p-p38, and p-ERK were also significantly increased in vehicle group than those in sham group (P < 0.05). However, UCF-101 treatment could markedly weaken the neurologic deficit with lower scores and improve pathological condition. After UCF-101 treatment, TUNEL positive neurons as well as the expression of caspase 3 were significantly decreased than those in vehicle group (P < 0.05). Besides, p-p38 was decreased while p-ERK was increased in UCF-101 group than those in vehicle group (P < 0.05). Therefore, we concluded that the protective effects of UCF-101 might be associated with apoptosis process and MAPK signaling pathway in the CIR-injured model.
Keywords: Apoptosis neurons; Cerebral ischemia–reperfusion; MAPK; UCF-101.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
UCF-101, a novel Omi/HtrA2 inhibitor, protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2009 Jun;292(6):854-61. doi: 10.1002/ar.20910. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2009. PMID: 19462455
-
Influence of miR-34a on cerebral neuronal apoptosis in rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion through the Notch1 signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Sep;23(18):8049-8057. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201909_19021. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31599430
-
Ucf-101 alleviates Ischaemia/Reperfusion induced retinal inflammation and injury via suppressing oxidative damage.J Mol Histol. 2024 Aug;55(4):455-464. doi: 10.1007/s10735-024-10213-5. Epub 2024 Jun 15. J Mol Histol. 2024. PMID: 38877338
-
MiR-125b blocks Bax/Cytochrome C/Caspase-3 apoptotic signaling pathway in rat models of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting p53.Neurol Res. 2018 Oct;40(10):828-837. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2018.1488654. Epub 2018 Jun 29. Neurol Res. 2018. PMID: 29956588
-
All-Trans Retinoic Acid Ameliorates the Early Experimental Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Inhibiting the Loss of the Blood-Brain Barrier via the JNK/P38MAPK Signaling Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2018 Jun;43(6):1283-1296. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2545-4. Epub 2018 May 25. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 29802528
Cited by
-
PD98059 protects SH-SY5Y cells against oxidative stress in oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion.Transl Neurosci. 2023 Sep 6;14(1):20220300. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0300. eCollection 2023 Jan 1. Transl Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37719747 Free PMC article.
-
High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway.Open Life Sci. 2025 Mar 6;20(1):20220971. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0971. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40059880 Free PMC article.
-
Coriolus versicolor polysaccharides (CVP) regulates neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via the p38MAPK signaling pathway.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Sep;8(18):1168. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-5759. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33241017 Free PMC article.
-
UCF-101 ameliorates traumatic brain injury by promoting microglia M2 polarization via AMPK/NF-κB pathways in LPS-induced BV2 cells.J Mol Histol. 2024 Dec 30;56(1):61. doi: 10.1007/s10735-024-10336-9. J Mol Histol. 2024. PMID: 39739143
-
Sulbactam Protects Hippocampal Neurons Against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation by Up-Regulating Astrocytic GLT-1 via p38 MAPK Signal Pathway.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Aug 15;11:281. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00281. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30158854 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Althaus J, Siegelin MD, Dehghani F, Cilenti L, Zervos AS, Rami A (2007) The serine protease Omi/HtrA2 is involved in XIAP cleavage and in neuronal cell death following focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Neurochem Int 50(1):172–180. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2006.07.018 - PubMed
-
- Ashraf MI, Ebner M, Wallner C, Haller M, Khalid S, Schwelberger H, Koziel K, Enthammer M, Hermann M, Sickinger S, Soleiman A, Steger C, Vallant S, Sucher R, Brandacher G, Santer P, Dragun D, Troppmair J (2014) A p38MAPK/MK2 signaling pathway leading to redox stress, cell death and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Commun Signal 12:6. doi:10.1186/1478-811X-12-6 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhuiyan MS, Fukunaga K (2009) Mitochondrial serine protease HtrA2/Omi as a potential therapeutic target. Curr Drug Targets 10(4):372–383 - PubMed
-
- Bu X, Huang P, Qi Z, Zhang N, Han S, Fang L, Li J (2007) Cell type-specific activation of p38 MAPK in the brain regions of hypoxic preconditioned mice. Neurochem Int 51(8):459–466. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2007.04.028 - PubMed
-
- Campos-Gonzalez R, Kindy MS (1992) Tyrosine phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein kinase after transient ischemia in the gerbil brain. J Neurochem 59(5):1955–1958 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

