Significant association of serum creatinine with HbA1C in impaired glucose tolerant Pakistani subjects
- PMID: 26430445
- PMCID: PMC4590356
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.314.7063
Significant association of serum creatinine with HbA1C in impaired glucose tolerant Pakistani subjects
Abstract
Objective: The present study was conducted to assess the serum concentration of creatinine and determine its relationship with potential risk factors of diabetes in Impaired Glucose tolerance subjects.
Methods: This cross sectional study was conducted on 100 IGT patients who attended Amin Hayat diabetic center in Lahore from January 2011- June 2011. Patients with age group 34-67 years, (both sexes) were included in the study. Different demographic parameters as age, BMI, WHR, B.P, personal history and socioeconomic status were recorded. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test was performed. The biochemical parameters including HbA1c, lipid profile, urea, uric acid, creatinine and bilirubin level were measured by chemistry analyzer.
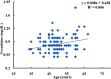
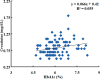
Results: A strong correlation between creatinine and HbA1c was observed. The level of creatinine was also significantly associated with age in IGT subjects. Creatinine is non-significantly correlated with Cholesterol, LDL-Chol and TG while negatively significantly associated with BMI, fasting blood glucose and HDL-Chol.
Conclusion: The present study concluded significant association of serum creatinine with HbA1c, BMI and HDL cholesterol.
Keywords: HbA1c; IGT; Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT); Serum creatinine.
Figures
References
-
- Rao SS, Disraeli P, Mcgregor T. Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Impaired Fasting Glucose. Am Fam Physician. 2004;69(8):1961–1968. - PubMed
-
- Vendrame F, Gottlieb PA. Prediabetes: prediction and prevention trials. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2004;33:75–92. - PubMed
-
- Pascot A, Despre´s JP, Lemieux I, Bergeron J, Nadeau A, Prud’homme D, et al. Deterioration of the Metabolic Risk Profile in Women. Respective contributions of impaired glucose tolerance and visceral fat accumulation. Diabetes Care. 2001;24(5):1. doi: 10.2337/diacare.24.5.902. - PubMed
-
- Yonemura K, Takahira R, Yonekawa O, Wada N, Hishida A. The diagnostic value of serum concentrations of 2-(alpha-mannopyranosyl)-Ltryptophan for normal renal function. Kidney Int. 2004;65:1395–1399. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00521.x. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous