Identification of Pol IV and RDR2-dependent precursors of 24 nt siRNAs guiding de novo DNA methylation in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 26430765
- PMCID: PMC4716838
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.09591
Identification of Pol IV and RDR2-dependent precursors of 24 nt siRNAs guiding de novo DNA methylation in Arabidopsis
Abstract
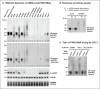
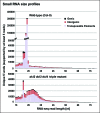
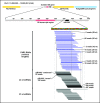
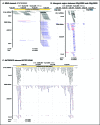
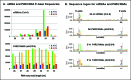
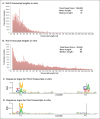
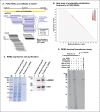
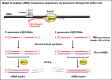
In Arabidopsis thaliana, abundant 24 nucleotide small interfering RNAs (24 nt siRNA) guide the cytosine methylation and silencing of transposons and a subset of genes. 24 nt siRNA biogenesis requires nuclear RNA polymerase IV (Pol IV), RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 2 (RDR2) and DICER-like 3 (DCL3). However, siRNA precursors are mostly undefined. We identified Pol IV and RDR2-dependent RNAs (P4R2 RNAs) that accumulate in dcl3 mutants and are diced into 24 nt RNAs by DCL3 in vitro. P4R2 RNAs are mostly 26-45 nt and initiate with a purine adjacent to a pyrimidine, characteristics shared by Pol IV transcripts generated in vitro. RDR2 terminal transferase activity, also demonstrated in vitro, may account for occasional non-templated nucleotides at P4R2 RNA 3' termini. The 24 nt siRNAs primarily correspond to the 5' or 3' ends of P4R2 RNAs, suggesting a model whereby siRNAs are generated from either end of P4R2 duplexes by single dicing events.
Keywords: RNA interference; RNA silencing; RNA-directed DNA methylation; arabidopsis; chromosomes; epigenetics; genes; noncoding RNA; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Blevins T, Rajeswaran R, Shivaprasad PV, Beknazariants D, Si-Ammour A, Park H-S, Vazquez F, Robertson D, Meins F, Hohn T, Pooggin MM. Four plant dicers mediate viral small RNA biogenesis and DNA virus induced silencing. Nucleic Acids Research. 2006;34:6233–6246. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl886. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blevins T, Podicheti R, Pikaard C. Pol IV and RDR2- dependent precursors of 24 nt siRNAs NCBI sequence read archive SRP059814, accession PRJNA287854. http://trace.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Traces/sra/?study=SRP059814 2015 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

