Adult Mammalian Neural Stem Cells and Neurogenesis: Five Decades Later
- PMID: 26431181
- PMCID: PMC4683085
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.09.003
Adult Mammalian Neural Stem Cells and Neurogenesis: Five Decades Later
Abstract
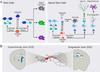
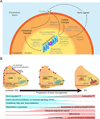
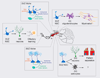
Adult somatic stem cells in various organs maintain homeostatic tissue regeneration and enhance plasticity. Since its initial discovery five decades ago, investigations of adult neurogenesis and neural stem cells have led to an established and expanding field that has significantly influenced many facets of neuroscience, developmental biology, and regenerative medicine. Here we review recent progress and focus on questions related to adult mammalian neural stem cells that also apply to other somatic stem cells. We further discuss emerging topics that are guiding the field toward better understanding adult neural stem cells and ultimately applying these principles to improve human health.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Akers KG, Martinez-Canabal A, Restivo L, Yiu AP, De Cristofaro A, Hsiang HL, Wheeler AL, Guskjolen A, Niibori Y, Shoji H, et al. Hippocampal neurogenesis regulates forgetting during adulthood and infancy. Science. 2014;344:598–602. - PubMed
-
- Alfonso J, Le Magueresse C, Zuccotti A, Khodosevich K, Monyer H. Diazepam binding inhibitor promotes progenitor proliferation in the postnatal SVZ by reducing GABA signaling. Cell stem cell. 2012;10:76–87. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Das GD. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. The Journal of comparative neurology. 1965;124:319–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

