Subcellular localization of PUMA regulates its pro-apoptotic activity in Burkitt's lymphoma B cells
- PMID: 26431330
- PMCID: PMC4741992
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5901
Subcellular localization of PUMA regulates its pro-apoptotic activity in Burkitt's lymphoma B cells
Abstract
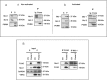
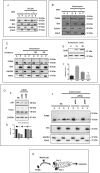
The BH3-only protein PUMA (p53-upregulated modulator of apoptosis) is a major regulator of apoptosis. It belongs to the Bcl-2 family of proteins responsible for maintaining mitochondrial outer membrane integrity by controlling the intrinsic (mitochondrial) apoptotic pathway. We describe here a new pathway regulating PUMA activation through the control of its subcellular distribution. Surprisingly, neither PUMA upregulation in normal activated human B lymphocytes nor high levels of PUMA in Burkitt's lymphoma (BL) were associated with cell death. We show that PUMA is localized to the cytosol in these cells. By contrast, various apoptosis-triggering signals were found to promote the translocation of PUMA to the mitochondria in these cells, leading to their death by apoptosis. This apoptosis was associated with the binding of mitochondrial PUMA to anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family, such as Bcl-2 and Mcl-1. This translocation was caspase-independent but was prevented by inhibiting or knocking down the expression of the MAPK kinase p38. Our data suggest that the accumulation of PUMA in the cytosol may be important for the participation of this protein in apoptosis without the need for prior transcription. This regulatory pathway may be an important feature of differentiation and tumorigenic processes.
Keywords: Burkitt’s lymphoma; PUMA; apoptosis; mitochondria; translocation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing financial interests relating to this work to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TGFbeta-mediated apoptosis of Burkitt's lymphoma BL41 cells is associated with the relocation of mitochondrial BimEL.Oncogene. 2008 May 29;27(24):3446-56. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1211009. Epub 2008 Jan 14. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18193085
-
β-elemene against Burkitt's lymphoma via activation of PUMA mediated apoptotic pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Oct;106:1557-1562. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.124. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30119230
-
Puma(*)Mcl-1 interaction is not sufficient to prevent rapid degradation of Mcl-1.Oncogene. 2005 Nov 3;24(48):7224-37. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208873. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 16007132
-
PUMA, a critical mediator of cell death--one decade on from its discovery.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2012 Dec;17(4):646-69. doi: 10.2478/s11658-012-0032-5. Epub 2012 Sep 20. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2012. PMID: 23001513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PUMA cooperates with direct activator proteins to promote mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and apoptosis.Cell Cycle. 2009 Sep 1;8(17):2692-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.17.9412. Epub 2009 Sep 2. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19652530 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bufalin Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Osteosarcoma Cells by Downregulating MicroRNA-221.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:7319464. doi: 10.1155/2016/7319464. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 28074104 Free PMC article.
-
MEK inhibitors induce apoptosis via FoxO3a-dependent PUMA induction in colorectal cancer cells.Oncogenesis. 2018 Sep 7;7(9):67. doi: 10.1038/s41389-018-0078-y. Oncogenesis. 2018. Retraction in: Oncogenesis. 2024 Nov 21;13(1):41. doi: 10.1038/s41389-024-00543-0. PMID: 30190455 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Anti-miR-518d-5p overcomes liver tumor cell death resistance through mitochondrial activity.Cell Death Dis. 2021 May 28;12(6):555. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03827-0. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34050139 Free PMC article.
-
The role of ROS and subsequent DNA-damage response in PUMA-induced apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 4;8(14):23492-23506. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15626. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423586 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of microRNA‑494 inhibits cell proliferation in lung squamous cell carcinoma via the induction of PUMA‑α‑mediated apoptosis.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Apr 11;25(6):242. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.11941. eCollection 2023 Jun. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37153893 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galonek HL, Hardwick JM. Upgrading the BCL-2 network. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:1317–1319. - PubMed
-
- Youle RJ, Strasser A. The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:47–59. - PubMed
-
- Huang DC, Strasser A. BH3-Only proteins-essential initiators of apoptotic cell death. Cell. 2000;103:839–842. - PubMed
-
- Nakano K, Vousden KH. PUMA, a novel proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Mol Cell. 2001;7:683–694. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, Zhang L, Hwang PM, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. PUMA induces the rapid apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cell. 2001;7:673–682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

