An integrated map of structural variation in 2,504 human genomes
- PMID: 26432246
- PMCID: PMC4617611
- DOI: 10.1038/nature15394
An integrated map of structural variation in 2,504 human genomes
Abstract
Structural variants are implicated in numerous diseases and make up the majority of varying nucleotides among human genomes. Here we describe an integrated set of eight structural variant classes comprising both balanced and unbalanced variants, which we constructed using short-read DNA sequencing data and statistically phased onto haplotype blocks in 26 human populations. Analysing this set, we identify numerous gene-intersecting structural variants exhibiting population stratification and describe naturally occurring homozygous gene knockouts that suggest the dispensability of a variety of human genes. We demonstrate that structural variants are enriched on haplotypes identified by genome-wide association studies and exhibit enrichment for expression quantitative trait loci. Additionally, we uncover appreciable levels of structural variant complexity at different scales, including genic loci subject to clusters of repeated rearrangement and complex structural variants with multiple breakpoints likely to have formed through individual mutational events. Our catalogue will enhance future studies into structural variant demography, functional impact and disease association.
Conflict of interest statement
E.E.E. is on the scientific advisory board (SAB) of DNAnexus, Inc. and is a consultant for Kunming University of Science and Technology (KUST) as part of the 1000 China Talent Program. P.F. is on the SAB of Omicia, Inc.
Figures
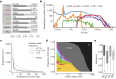



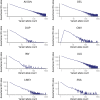







Comment in
-
Human genomics: The end of the start for population sequencing.Nature. 2015 Oct 1;526(7571):52-3. doi: 10.1038/526052a. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26432243 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- S10 RR029676/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG007068/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG002898/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- RR19895/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U41HG007497/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM059290/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR029676-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA166661/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HG007497/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002385/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG007068/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002898/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P01HG007497/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG007497/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM59290/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR019895/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- WT104947/Z/14/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- T32 GM008666/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- WT085532/Z/08/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01CA166661/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 104947/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 085532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

