New insights into the enzymatic role of EF-G in ribosome recycling
- PMID: 26432831
- PMCID: PMC4666400
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv995
New insights into the enzymatic role of EF-G in ribosome recycling
Abstract
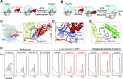
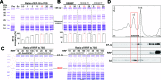
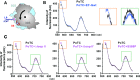
During translation, elongation factor G (EF-G) plays a catalytic role in tRNA translocation and a facilitative role in ribosome recycling. By stabilizing the rotated ribosome and interacting with ribosome recycling factor (RRF), EF-G was hypothesized to induce the domain rotations of RRF, which subsequently performs the function of splitting the major intersubunit bridges and thus separates the ribosome into subunits for recycling. Here, with systematic mutagenesis, FRET analysis and cryo-EM single particle approach, we analyzed the interplay between EF-G/RRF and post termination complex (PoTC). Our data reveal that the two conserved loops (loop I and II) at the tip region of EF-G domain IV possess distinct roles in tRNA translocation and ribosome recycling. Specifically, loop II might be directly involved in disrupting the main intersubunit bridge B2a between helix 44 (h44 from the 30S subunit) and helix 69 (H69 from the 50S subunit) in PoTC. Therefore, our data suggest a new ribosome recycling mechanism which requires an active involvement of EF-G. In addition to supporting RRF, EF-G plays an enzymatic role in destabilizing B2a via its loop II.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structural insights into initial and intermediate steps of the ribosome-recycling process.EMBO J. 2012 Apr 4;31(7):1836-46. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.22. Epub 2012 Mar 2. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22388519 Free PMC article.
-
Specific interaction between EF-G and RRF and its implication for GTP-dependent ribosome splitting into subunits.J Mol Biol. 2007 Dec 14;374(5):1345-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Oct 16. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17996252 Free PMC article.
-
Splitting of the posttermination ribosome into subunits by the concerted action of RRF and EF-G.Mol Cell. 2005 Jun 10;18(6):675-86. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.05.016. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15949442
-
[Ribosome recycling revisited].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2006 Jul-Aug;40(4):742-50. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2006. PMID: 16913233 Review. Russian.
-
Structural insights into ribosome translocation.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016 Sep;7(5):620-36. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1354. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016. PMID: 27117863 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unlocking Enhanced Efficacy of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Microb Biotechnol. 2025 Jun;18(6):e70174. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.70174. Microb Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40448301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel GFM2 variants associated with early-onset neurological presentations of mitochondrial disease and impaired expression of OXPHOS subunits.Neurogenetics. 2017 Dec;18(4):227-235. doi: 10.1007/s10048-017-0526-4. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Neurogenetics. 2017. PMID: 29075935 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription regulates ribosome hibernation.Mol Microbiol. 2021 Aug;116(2):663-673. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14762. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Mol Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34152658 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in Gene fusA1 as a Novel Mechanism of Aminoglycoside Resistance in Clinical Strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Jan 25;62(2):e01835-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01835-17. Print 2018 Feb. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29133559 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted Mechanism of Amicoumacin A Inhibition of Bacterial Translation.Front Microbiol. 2021 Feb 12;12:618857. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.618857. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33643246 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yamamoto H., Qin Y., Achenbach J., Li C., Kijek J., Spahn C.M., Nierhaus K.H. EF-G and EF4: translocation and back-translocation on the bacterial ribosome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014;12:89–100. - PubMed
-
- Ramakrishnan V. Ribosome structure and the mechanism of translation. Cell. 2002;108:557–572. - PubMed
-
- Hirokawa G., Demeshkina N., Iwakura N., Kaji H., Kaji A. The ribosome-recycling step: consensus or controversy? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006;31:143–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

