Homeostasis and its disruption in the lung microbiome
- PMID: 26432870
- PMCID: PMC4652146
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00279.2015
Homeostasis and its disruption in the lung microbiome
Abstract
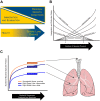
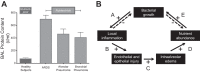
The disciplines of physiology and ecology are united by the shared centrality of the concept of homeostasis: the stability of a complex system via internal mechanisms of self-regulation, resilient to external perturbation. In the past decade, these fields of study have been bridged by the discovery of the lung microbiome. The respiratory tract, long considered sterile, is in fact a dynamic ecosystem of microbiota, intimately associated with the host inflammatory response, altered in disease states. If the microbiome is a "newly discovered organ," ecology is the language we use to explain how it establishes, maintains, and loses homeostasis. In this essay, we review recent insights into the feedback mechanisms by which the lung microbiome and the host response are regulated in health and dysregulated in acute and chronic lung disease. We propose three explanatory models supported by recent studies: the adapted island model of lung biogeography, nutritional homeostasis at the host-microbiome interface, and interkingdom signaling and the community stress response.
Keywords: 16S; culture-independent; ecology; equilibrium; homeostasis; lung; microbial ecology; physiology; pulmonary.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Amberson JB. A clinical consideration of abscesses and cavities of the lung. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp 94: 227–237, 1954. - PubMed
-
- Andersson SGE, Zomorodipour A, Andersson JO, Sicheritz-Ponten T, Alsmark UCM, Podowski RM, Naslund AK, Eriksson AS, Winkler HH, Kurland CG. The genome sequence of Rickettsia prowazekii and the origin of mitochondria. Nature 396: 133–140, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Bernard C. Leçons sur les pheínomeÌnes de la vie communs aux animaux et veígeítaux. Paris: Baillere, 1878.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

