Infection and characterization of Toxoplasma gondii in human induced neurons from patients with brain disorders and healthy controls
- PMID: 26432947
- PMCID: PMC4758902
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micinf.2015.09.023
Infection and characterization of Toxoplasma gondii in human induced neurons from patients with brain disorders and healthy controls
Abstract
Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite capable of establishing persistent infection within the brain. Serological studies in humans have linked exposure to Toxoplasma to neuropsychiatric disorders. However, serological studies have not elucidated the related molecular mechanisms within neuronal cells. To address this question, we used human induced neuronal cells derived from peripheral fibroblasts of healthy individuals and patients with genetically-defined brain disorders (i.e. childhood-onset schizophrenia with disease-associated copy number variations). Parasite infection was characterized by differential detection of tachyzoites and tissue cysts in induced neuronal cells. This approach may aid study of molecular mechanisms underlying individual predisposition to Toxoplasma infection linked to neuropathology of brain disorders.
Keywords: Brain disorders; Cysts; Induced neuronal cells; Schizophrenia; Tachyzoites; Toxoplasma gondii.
Copyright © 2015 Institut Pasteur. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have not competing interests for this specific manuscript.
Figures
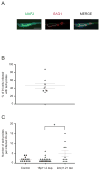
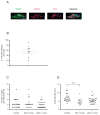
Similar articles
-
[Toxoplasma gondii: a potential role in the genesis of psychiatric disorders].Encephale. 2013 Feb;39(1):38-43. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2012.06.014. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Encephale. 2013. PMID: 23095600 Review. French.
-
Growth and development of Toxoplasma gondii in human neurons and astrocytes.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1996 Nov;55(11):1150-6. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199611000-00006. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8939198
-
Primary brain cell infection by Toxoplasma gondii reveals the extent and dynamics of parasite differentiation and its impact on neuron biology.Open Biol. 2021 Oct;11(10):210053. doi: 10.1098/rsob.210053. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Open Biol. 2021. PMID: 34610266 Free PMC article.
-
Host cells of Toxoplasma gondii encystation in infected primary culture from mouse brain.Parasitol Res. 1997;83(7):637-41. doi: 10.1007/s004360050311. Parasitol Res. 1997. PMID: 9272550
-
The known and missing links between Toxoplasma gondii and schizophrenia.Metab Brain Dis. 2016 Aug;31(4):749-59. doi: 10.1007/s11011-016-9822-1. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Metab Brain Dis. 2016. PMID: 27041387 Review.
Cited by
-
Direct Neuronal Reprogramming for Disease Modeling Studies Using Patient-Derived Neurons: What Have We Learned?Front Neurosci. 2017 Sep 28;11:530. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00530. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29033781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of in vitro derived human neuronal models to study host-parasite interactions of Toxoplasma gondii in neurons and neuropathogenesis of chronic toxoplasmosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Mar 8;13:1129451. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1129451. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36968101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Depletion of Intracellular Glutamine Pools Triggers Toxoplasma gondii Stage Conversion in Human Glutamatergic Neurons.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jan 13;11:788303. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.788303. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35096641 Free PMC article.
-
Forskolin rapidly enhances neuron-like morphological change of directly induced-neuronal cells from neurofibromatosis type 1 patients.Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2020 Dec;40(4):396-400. doi: 10.1002/npr2.12144. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2020. PMID: 33037790 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated gene expressions of MEX3D, FOS and BCL2 in human induced-neuronal (iN) cells from NF1 patients: a pilot study.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 24;7(1):13905. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14440-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29066822 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hill DE, Chirukandoth S, Dubey JP. Biology and epidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii in man and animals. Anim Health Res Rev. 2005;6:41–61. - PubMed
-
- Miman O, Mutlu EA, Ozcan O, Atambay M, Karlidag R, Unal S. Is there any role of Toxoplasma gondii in the etiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder? Psychiatry Res. 2010;177:263–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P50 MH094268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-069853/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-092443/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH069853/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH105660/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH085226/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-084018/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-085226/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-094268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 MH088753/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH092443/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R00 MH093458/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-105660/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MH084018/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-088753/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

