Differential Responses of Plasma Adropin Concentrations To Dietary Glucose or Fructose Consumption In Humans
- PMID: 26435060
- PMCID: PMC4592955
- DOI: 10.1038/srep14691
Differential Responses of Plasma Adropin Concentrations To Dietary Glucose or Fructose Consumption In Humans
Abstract
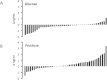
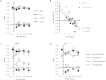
Adropin is a peptide hormone encoded by the Energy Homeostasis Associated (ENHO) gene whose physiological role in humans remains incompletely defined. Here we investigated the impact of dietary interventions that affect systemic glucose and lipid metabolism on plasma adropin concentrations in humans. Consumption of glucose or fructose as 25% of daily energy requirements (E) differentially affected plasma adropin concentrations (P < 0.005) irrespective of duration, sex or age. Glucose consumption reduced plasma adropin from 3.55 ± 0.26 to 3.28 ± 0.23 ng/ml (N = 42). Fructose consumption increased plasma adropin from 3.63 ± 0.29 to 3.93 ± 0.34 ng/ml (N = 45). Consumption of high fructose corn syrup (HFCS) as 25% E had no effect (3.43 ± 0.32 versus 3.39 ± 0.24 ng/ml, N = 26). Overall, the effect of glucose, HFCS and fructose on circulating adropin concentrations were similar to those observed on postprandial plasma triglyceride concentrations. Furthermore, increases in plasma adropin levels with fructose intake were most robust in individuals exhibiting hypertriglyceridemia. Individuals with low plasma adropin concentrations also exhibited rapid increases in plasma levels following consumption of breakfasts supplemented with lipids. These are the first results linking plasma adropin levels with dietary sugar intake in humans, with the impact of fructose consumption linked to systemic triglyceride metabolism. In addition, dietary fat intake may also increase circulating adropin concentrations.
Figures


References
-
- Lovren F. et al. Adropin is a novel regulator of endothelial function. Circulation 122, S185–92 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1R01 HL091333/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL121324/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01 HL075675/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD051958/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK26687/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01 HL107256/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024146/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075675/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL107256/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091333/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK026687/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

