Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay: Degradation of Defective Transcripts Is Only Part of the Story
- PMID: 26436458
- PMCID: PMC4837945
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-genet-112414-054639
Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay: Degradation of Defective Transcripts Is Only Part of the Story
Abstract
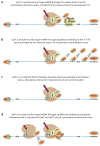
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) is a eukaryotic surveillance mechanism that monitors cytoplasmic mRNA translation and targets mRNAs undergoing premature translation termination for rapid degradation. From yeasts to humans, activation of NMD requires the function of the three conserved Upf factors: Upf1, Upf2, and Upf3. Here, we summarize the progress in our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of NMD in several model systems and discuss recent experiments that address the roles of Upf1, the principal regulator of NMD, in the initial targeting and final degradation of NMD-susceptible mRNAs. We propose a unified model for NMD in which the Upf factors provide several functions during premature termination, including the stimulation of release factor activity and the dissociation and recycling of ribosomal subunits. In this model, the ultimate degradation of the mRNA is the last step in a complex premature termination process.
Keywords: Upf proteins; quality control; ribosome dissociation; translation termination.
Figures



References
-
- Alkalaeva EZ, Pisarev AV, Frolova LY, Kisselev LL, Pestova TV. In vitro reconstitution of eukaryotic translation reveals cooperativity between release factors eRF1 and eRF3. Cell. 2006;125:1125–36. - PubMed
-
- Altamura N, Groudinsky O, Dujardin G, Slonimski PP. NAM7 nuclear gene encodes a novel member of a family of helicases with a Zn-ligand motif and is involved in mitochondrial functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1992;224:575–87. - PubMed
-
- Amrani N, Ganesan R, Kervestin S, Mangus DA, Ghosh S, Jacobson A. A faux 3′-UTR promotes aberrant termination and triggers nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Nature. 2004;432:112–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

