Orthogonal gene knockout and activation with a catalytically active Cas9 nuclease
- PMID: 26436575
- PMCID: PMC4747789
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3390
Orthogonal gene knockout and activation with a catalytically active Cas9 nuclease
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Orthogonal gene knockout and activation with a catalytically active Cas9 nuclease.Nat Biotechnol. 2016 Apr;34(4):441. doi: 10.1038/nbt0416-441a. Nat Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27054997 No abstract available.
Abstract
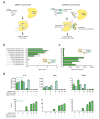
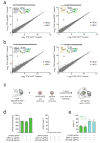
We have developed a CRISPR-based method that uses catalytically active Cas9 and distinct single guide (sgRNA) constructs to knock out and activate different genes in the same cell. These sgRNAs, with 14- to 15-bp target sequences and MS2 binding loops, can activate gene expression using an active Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9 nuclease, without inducing double-stranded breaks. We use these 'dead RNAs' to perform orthogonal gene knockout and transcriptional activation in human cells.
Conflict of interest statement
JED, OOA, FZ, and SK have filed intellectual property related to material described in this publication.
Figures
References
Methods References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

