Parasympathomimetic drugs for the treatment of salivary gland dysfunction due to radiotherapy
- PMID: 26436597
- PMCID: PMC6599847
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003782.pub3
Parasympathomimetic drugs for the treatment of salivary gland dysfunction due to radiotherapy
Abstract
Background: This is an updated version of the original Cochrane review on parasympathomimetic drugs for the treatment of salivary gland dysfunction due to radiotherapy (published in Issue 3, 2007). Salivary gland dysfunction is a predictable side effect of radiotherapy to the head and neck region. Pilocarpine hydrochloride (a choline ester) is licensed in many countries for the treatment of radiation-induced salivary gland dysfunction. Other parasympathomimetics have also been used 'off licence' in the treatment of this condition.
Objectives: To determine the efficacy and tolerability of parasympathomimetic drugs in the treatment of radiation-induced salivary gland dysfunction (specifically radiation-induced xerostomia).
Search methods: For this update, we ran searches of the Cochrane Oral Health Group Trials Register, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL 2015, Issue 6), MEDLINE, EMBASE, and CINAHL in July 2015. We checked the reference lists of retrieved articles for additional studies, contacted experts in the field for unpublished and ongoing trials, and contacted relevant pharmaceutical companies for unpublished and ongoing trials.
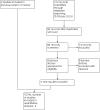
Selection criteria: The selection criteria for the review were: 1) randomised controlled trials; 2) people suffering from radiation-induced salivary gland dysfunction; 3) people treated with parasympathomimetic drugs; and 4) assessable data available on primary outcome measure.
Data collection and analysis: The two review authors independently collected data from the full-text version of relevant papers including: 1) citation details; 2) participants; 3) interventions; 4) assessments; 5) outcomes (that is efficacy, tolerability); and 6) quality issues.Due to a lack of appropriate data, we were unable to perform a meta-analysis.
Main results: In the original review, three studies, including a total of 298 participants, fulfilled the inclusion criteria. All three studies involved the use of pilocarpine hydrochloride. We have included no additional studies in the update of the review; we have excluded eight additional studies.The data suggest that pilocarpine hydrochloride is more effective than placebo and at least as effective as artificial saliva. The response rate was 42% to 51%. The time to response was up to 12 weeks. The overall side effect rate was high, and side effects were the main reason for withdrawal (6% to 15% of participants taking 5 mg three times a day had to withdraw). The side effects were usually the result of generalised parasympathomimetic stimulation (for example sweating, headaches, urinary frequency, vasodilatation). Response rates were not dose dependent, but side effect rates were dose dependent.
Authors' conclusions: There is limited evidence to support the use of pilocarpine hydrochloride in the treatment of radiation-induced xerostomia. Currently, there is little evidence to support the use of other parasympathomimetic drugs in the treatment of radiation-induced xerostomia. Available studies suggest that approximately half of patients will respond, but side effects can be problematic. The conclusions of the update are the same as the conclusions of the original review, since no new relevant studies have been published in the interim.
Conflict of interest statement
Andrew Davies has no relevant conflicts of interest to declare. Jo Thompson has no relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Update of
-
Parasympathomimetic drugs for the treatment of salivary gland dysfunction due to radiotherapy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;(3):CD003782. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003782.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 05;(10):CD003782. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003782.pub3. PMID: 17636736 Updated.
Comment in
-
Parasympathomimetic drugs for dry mouth due to radiotherapy.Evid Based Dent. 2016 Sep;17(3):79. doi: 10.1038/sj.ebd.6401185. Evid Based Dent. 2016. PMID: 27767109
References
References to studies included in this review
Davies 1994 {published data only}
-
- Davies AN, Singer J. A comparison of artificial saliva and pilocarpine in radiation-induced xerostomia. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 1994;108(8):663-5. - PubMed
Johnson 1993 {published data only}
-
- Johnson JT, Ferretti GA, Nethery WJ, Valdez IH, Fox PC, Ng D, et al. Oral pilocarpine for post-irradiation xerostomia in patients with head and neck cancer. The New England Journal of Medicine 1993;329(6):390-5. - PubMed
-
- Rieke JW, Hafermann MD, Johnson JT, LeVeque FG, Iwamoto R, Steiger BW, et al. Oral pilocarpine for radiation-induced xerostomia: Integrated efficacy and safety results from two prospective randomized clinical trials. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics 1995;31(3):661-9. - PubMed
LeVeque 1993 {published data only}
-
- LeVeque FG, Montgomery M, Potter D, Zimmer MB, Rieke JW, Steiger BW. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-titration study of oral pilocarpine for treatment of radiation-induced xerostomia in head and neck cancer patients. Journal of Clinical Oncology 1993;11(6):1124-31. - PubMed
-
- Rieke JW, Hafermann MD, Johnson JT, LeVeque FG, Iwamoto R, Steiger BW. Oral pilocarpine for radiation-induced xerostomia: Integrated efficacy and safety results from two prospective randomized clinical trials. International Journal of Radition Oncology, Biology, Physics 1995;31(3):661-9. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abbasi 2013 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Chambers 2007a {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Chambers MS, Posner M, Jones CU, Biel MA, Hodge KM, Vitti R, et al. Cevimeline for the treatment of postirradiation xerostomia in patients with head and neck cancer. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics 2007;68(4):1102-9. - PubMed
Chambers 2007b {published data only}
-
- Chambers MS, Jones CU, Biel MA, Weber RS, Hodge KM, Chen Y, et al. Open-label, long-term safety study of cevimeline in the treatment of postirradiation xerostomia. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics 2007;69(5):1369-76. - PubMed
Chitapanarux 2008 {published data only}
-
- Chitapanarux I, Kamnerdsupaphon P, Tharavichitkul E, Sumitsawan Y, Sittitrai P, Pattaraskulchai T, et al. Effect of oral pilocarpine on post-irradiation xerostomia in head and neck cancer patients: a single-center, single-blind clinical trial. Journal of Medical Association of Thailand 2008;91(9):1410-4. - PubMed
Cooper 1999 {published data only}
-
- Cooper RA, Cowan RA, Owens SE, Jeans SP, Roberts JK, Hillel PG. Does salivary gland scintigraphy predict response to pilocarpine in patients with post-radiotherapy xerostomia? European Journal of Nuclear Medicine 1999;26(3):220-5. - PubMed
Epstein 1987 {published data only}
-
- Epstein JB, Schubert MM. Synergistic effect of sialagogues in management of xerostomia after radiation therapy. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology 1987;64(2):179-82. - PubMed
Epstein 1994 {published data only}
-
- Epstein JB, Burchell JL, Emerton S, Le ND, Silverman S. A clinical trial of bethanechol in patients with xerostomia after radiation therapy. A pilot study. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology 1994;77(6):610-4. - PubMed
Ferguson 1991 {published data only}
-
- Ferguson MM, Hayes P, Highton J, Jones DS, MacFadyen EE, Palmer DG. Pilocarpine oral solution. British Dental Journal 1991;170(7):251. - PubMed
Fox 1991 {published data only}
-
- Fox PC, Atkinson JC, Macynski AA, Wolff A, Kung DS, Valdez IH, et al. Pilocarpine treatment of salivary gland hypofunction and dry mouth (xerostomia). Archives of Internal Medicine 1991;151(6):1149-52. - PubMed
Frydrych 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Frydrych AM, Davies GR, Slack-Smith LM, Heywood J. An investigation into the use of pilocarpine as a sialagogue in patients with radiation induced xerostomia. Australian Dental Journal 2002;47(3):249-53. - PubMed
Gorsky 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gorsky M, Epstein JB, Parry J, Epstein MS, Le ND, Silverman Jr S. The efficacy of pilocarpine and bethanechol upon saliva production in cancer patients with hyposalivation following radiation therapy. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and Endodontics 2004;97(2):190-5. - PubMed
Greenspan 1987 {published data only}
-
- Greenspan D, Daniels TE. Effectiveness of pilocarpine in postradiation xerostomia. Cancer 1987;59(6):1123-5. - PubMed
Hamlar 1996 {published data only}
-
- Hamlar DD, Schuller DE, Gahbauer RA, Buerki RA, Staubus AE, Hall J. Determination of the efficacy of topical oral pilocarpine for postirradiation xerostomia in patients with head and neck carcinoma. Laryngoscope 1996;106(8):972-6. - PubMed
Horiot 2000 {published data only}
-
- Horiot JC, Lipinski F, Schraub S, Maulard-Durdux C, Bensadoun RJ, Ardiet JM. Post-radiation severe xerostomia relieved by pilocarpine: a prospective French cooperative study. Radiotherapy and Oncology 2000;55(3):233-9. - PubMed
Jacobs 1996 {published data only}
-
- Jacobs CD, Van Der Pas M. A multicenter maintenance study of oral pilocarpine tablets for radiation-induced xerostomia. Oncology (Huntington) 1996;10(3 Suppl):16-20. - PubMed
Joensuu 1993 {published data only}
-
- Joensuu H, Bostrom P, Makkonen T. Pilocarpine and carbacholine in treatment of radiation-induced xerostomia. Radiotherapy and Oncology 1993;26(1):33-7. - PubMed
Konno 2007 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Konno A, Nishio M, Origasa H. Oral pilocarpine for radiation-induced xerostomia - a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Japanese Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2007;35 (Suppl 2):S131-40.
Leek 2002 {published data only}
-
- Leek H, Albertsson M. Pilocarpine treatment of xerostomia in head and neck patients. Micron 2002;33(2):153-5. - PubMed
MacCarthy 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- MacCarthy D, Moriarty M, Waldron D. The use of pilocarpine HCl in patients with post-radiation xerostomia - Report of a pilot study. (IADR abstract). Journal of Dental Research 1998;77(Spec Iss B):979.
Matsumoto 2000 {published data only}
-
- Matsumoto Y. Research on delayed damage after radiation therapy for head and neck patients. Shika Igaku 2000;63(1):15-22.
Mosqueda‐Taylor 2004 {published data only}
-
- Mosqueda-Taylor A, Luna-Ortiz K, Irigoyen-Camacho ME, Diaz-Franco MA, Coll-Munoz AM. Effect of pilocarpine hydrochloride on salivary production in previously irradiated head and neck cancer patients [Efecto del clorhidrato de pilocarpina como estimulante de la produccion salival en pacientes sometidos a radioterapia de cabeza y cuello]. Medicina Oral 2004;9(3):204-11. - PubMed
Nakamura 2009 {published data only}
-
- Nakamura N, Sasano N, Yamashita H, Igaki H, Shiraishi K, Terahara A, et al. Oral pilocarpine (5mg t.i.d) used for xerostomia causes adverse effects in Japanese. Auris Nasus Larynx 2009;36(3):310-3. - PubMed
Schuller 1989 {published data only}
-
- Schuller DE, Stevens P, Clausen KP, Olsen J, Gahbauer R, Martin M. Treatment of radiation side effects with oral pilocarpine. Journal of Surgical Oncology 1989;42(4):272-6. - PubMed
Singhal 1997 {published data only}
-
- Singhal S, Powles R, Treleaven J, Rattenbury H, Mehta J. Pilocarpine hydrochloride for symptomatic relief of xerostomia due to chronic graft-versus-host disease or total-body irradiation after bone-marrow transplantation for hematologic malignancies. Leukemia and Lymphoma 1997;24(5-6):539-43. - PubMed
Szabo 1985 {published data only}
-
- Szabo G. Treatment of xerostomia with pilocarpine. Based on 15 years experience and treatment of 500 patients [Xerostomia kezelese Pilocarpinnal]. Fogorvosi Szemle 1985;78(3):65-9. - PubMed
Witsell 2012 {published data only}
-
- Witsell D, Stinnett S, Chambers MS. Effectiveness of cevimeline to improve oral health in patients with postradiation xerostomia. Head and Neck 2012;34(8):1136-42. - PubMed
Wong 2015 {published data only}
-
- Wong RK, Deshmukh S, Wyatt G, Sagar S, Singh AK, Sultanem K, et al. Acupuncture-like transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation versus pilocarpine in treating radiation-induced xerostomia: results of RTOG 0537 phase 3 study. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics 2015 [Epub ahead of print]. - PMC - PubMed
Additional references
Aromdee 1996
-
- Aromdee C, Fawcett JP, Ferguson MM, Ledger R. Serum pilocarpine esterase activity and response to oral pilocarpine. Biochemical and Molecular Medicine 1996;59(1):57-61. - PubMed
Bjornstrom 1990
-
- Bjornstrom M, Axell T, Birkhed D. Comparison between saliva stimulants and saliva substitutes in patients with symptoms related to dry mouth. A multi-centre study. Swedish Dental Journal 1990;14(4):153-61. - PubMed
Chambers 2005
-
- Chambers M, Garden A, Lemon J, Kies M, Martin J. Oral complications of cancer treatment. In: Davies A, Finlay I, editors(s). Oral Care in Advanced Disease. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2005:171-84.
Davies 2005
-
- Davies A. Salivary gland dysfunction. In: Davies A, Finlay I, editors(s). Oral Care in Advanced Disease. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2005:97-113.
Dawes 1987
-
- Dawes C. Physiological factors affecting salivary flow rates, oral sugar clearance, and the sensation of dry mouth in man. Journal of Dental Research 1987;66(Spec Iss):648-53. - PubMed
Guchelaar 1997
-
- Guchelaar H-J, Vermes A, Meerwaldt JH. Radiation-induced xerostomia: pathophysiology, clinical course and supportive treatment. Supportive Care in Cancer 1997;5(4):281-8. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Jensen 2010
-
- Jensen SB, Pedersen AML, Vissink A, Andersen E, Brown CG, Davies AN, et al. A systematic review of salivary gland hypofunction and xerostomia induced by cancer therapies: prevalence, severity and impact on quality of life. Supportive Care in Cancer 2010;18:1039-60. - PubMed
Navazesh 1992
-
- Navazesh M, Christensen C, Brightman V. Clinical criteria for the diagnosis of salivary gland hypofunction. Journal of Dental Research 1992;71(7):1363-9. - PubMed
Pankhurst 1996
-
- Pankhurst CL, Smith EC, Rogers JO, Dunne SM, Jackson SH, Proctor G. Diagnosis and management of the dry mouth: Part 1. Dental Update 1996;23(2):56-62. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager. Version 5.3. The Nordic Cochrane Centre, Copenhagen: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Sreebny 1996
-
- Sreebny LM. Xerostomia: diagnosis, management and clinical complications. In: Edgar WM, O'Mullane DM, editors(s). Saliva and Oral Health. 2nd edition. London: British Dental Association, 1996:43-66.
Wiseman 1995
-
- Wiseman LR, Faulds D. Oral pilocarpine: a review of its pharmacological properties and clinical potential in xerostomia. Drugs 1995;49(1):143-55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous