PIK3CA mutations can initiate pancreatic tumorigenesis and are targetable with PI3K inhibitors
- PMID: 26436951
- PMCID: PMC4632089
- DOI: 10.1038/oncsis.2015.28
PIK3CA mutations can initiate pancreatic tumorigenesis and are targetable with PI3K inhibitors
Abstract
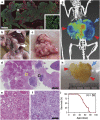
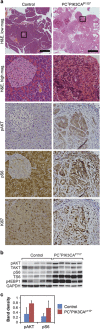
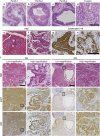
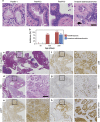
Aberrations in the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway have a key role in the pathogenesis of numerous cancers by altering cell growth, metabolism, proliferation and apoptosis. Interest in targeting the PI3K signaling cascade continues, as new agents are being clinically evaluated. PIK3CA mutations result in a constitutively active PI3K and are present in a subset of pancreatic cancers. Here we examine mutant PIK3CA-mediated pancreatic tumorigenesis and the response of PIK3CA mutant pancreatic cancers to dual PI3K/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibition. Two murine models were generated expressing a constitutively active PI3K within the pancreas. An increase in acinar-to-ductal metaplasia and pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasms (PanINs) was identified. In one model these lesions were detected as early as 10 days of age. Invasive pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma developed in these mice as early as 20 days of age. These cancers were highly sensitive to treatment with dual PI3K/mTOR inhibition. In the second model, PanINs and invasive cancer develop with a greater latency owing to a lesser degree of PI3K pathway activation in this murine model. In addition to PI3K pathway activation, increased ERK1/2 signaling is common in human pancreatic cancers. Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was also investigated in these models. Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 is demonstrated in the pre-neoplastic lesions and invasive cancers. This activation of ERK1/2 is diminished with dual PI3K/mTOR inhibition. In summary, PIK3CA mutations can initiate pancreatic tumorigenesis and these cancers are particularly sensitive to dual PI3K/mTOR inhibition. Future studies of PI3K pathway inhibitors for patients with PIK3CA mutant pancreatic cancers are warranted.
Figures

References
-
- 1Cancer Facts & Figures 2014. American Cancer Society: Atlanta, 2014.
-
- 2Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouche O, Guimbaud R, Becouarn Y et al. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 1817–1825. - PubMed
-
- 5Cataldo VD, Gibbons DL, Perez-Soler R, Quintas-Cardama A. Treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer with erlotinib or gefitinib. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 947–955. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

