Persistent behavioral effects following early life exposure to retinoic acid or valproic acid in zebrafish
- PMID: 26439099
- PMCID: PMC4753107
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuro.2015.10.001
Persistent behavioral effects following early life exposure to retinoic acid or valproic acid in zebrafish
Abstract
Background: Moderate to severe dysregulation in retinoid signaling during early development is associated with a constellation of physical malformations and/or neural tube defects, including spina bifida. It is thought that more subtle dysregulation of this system, which might be achievable via dietary (i.e. hypervitaminosis A) or pharmacological (i.e. valproic acid) exposure in humans, will manifest on behavioral domains including sociability, without overt physical abnormalities.
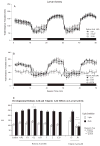
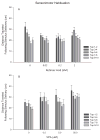
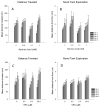
Methods: During early life, zebrafish were exposed to low doses of two chemicals that disrupt retinoid signaling. From 0 to 5dpf, larvae were reared in aqueous solutions containing retinoic acid (0, 0.02, 0.2 or 2nM) or valproic acid (0, 0.5, 5.0 or 50μM). One cohort of zebrafish was assessed using a locomotor activity screen at 6-dpf; another was reared to adulthood and assessed using a neurobehavioral test battery (startle habituation, novel tank exploration, shoaling, and predator escape/avoidance).
Results: There was no significant increase in the incidence of physical malformation among exposed fish compared to controls. Both retinoic acid and valproic acid exposures during development disrupted larval activity with persisting behavioral alterations later in life, primarily manifesting as decreased social affiliation.
Conclusions: Social behavior and some aspects of motor function were altered in exposed fish; the importance of examining emotional or psychological consequences of early life exposure to retinoid acting chemicals is discussed.
Keywords: Behavior; Cognition; Development; Retinoic acid; Social behavior; Vitamin A valproic acid; Zebrafish.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
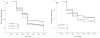

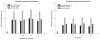
References
-
- Adams J. Structure-activity and dose-response relationships in the neural and behavioral teratogenesis of retinoids. Neurotoxicology & Teratology. 1993;15:193–202. - PubMed
-
- Adams J. The neurobehavioral teratology of retinoids: a 50-year history. Birth Defects Research. 2010;88:895–905. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad F, Noldus L, Tegelenbosch R, Richardson M. Zebrafish embryos and larvae in behavioural assays. Behaviour. 2012;149:1241–1281.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

