Molecular investigation of coexistent chronic myeloid leukaemia and peripheral T-cell lymphoma - a case report
- PMID: 26439403
- PMCID: PMC4594041
- DOI: 10.1038/srep14829
Molecular investigation of coexistent chronic myeloid leukaemia and peripheral T-cell lymphoma - a case report
Abstract
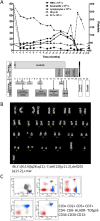
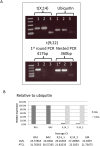
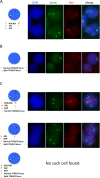
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a myeloproliferative neoplasm underlain by the formation of BCR-ABL1 - an aberrant tyrosine kinase - in the leukaemic blasts. Long-term survival rates in CML prior to the advent of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) were dismal, albeit the incidence of secondary malignancies was higher than that of age-matched population. Current figures confirm the safety of TKIs with conflicting data concerning the increased risk of secondary tumours. We postulate that care has to be taken when distinguishing between coexisting, secondary-to-treatment and second in sequence, but independent tumourigenic events, in order to achieve an unbiased picture of the adverse effects of novel treatments. To illustrate this point, we present a case of a patient in which CML and peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) coexisted, although the clinical presentation of the latter followed the achievement of major molecular response of CML to TKIs.
Figures
References
-
- Jabbour E. & Kantarjian H. Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2014 update on diagnosis, monitoring, and management. Am J Hematol 89, 547–556 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Yang K. & Fu L. W. Mechanisms of resistance to BCR-ABL TKIs and the therapeutic strategies: A review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 93, 277–92 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Duman B. B., Paydas S., Disel U., Besen A. & Gurkan E. Secondary malignancy after imatinib therapy: eight cases and review of the literature. Leuk Lymphoma 53, 1706–1708 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

