The Washington University Central Neuroimaging Data Archive
- PMID: 26439514
- PMCID: PMC4967044
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.09.060
The Washington University Central Neuroimaging Data Archive
Abstract
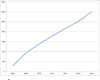
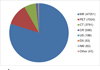
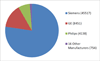
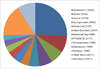
Since the early 2000's, much of the neuroimaging work at Washington University (WU) has been facilitated by the Central Neuroimaging Data Archive (CNDA), an XNAT-based imaging informatics system. The CNDA is uniquely related to XNAT, as it served as the original codebase for the XNAT open source platform. The CNDA hosts data acquired in over 1000 research studies, encompassing 36,000 subjects and more than 60,000 imaging sessions. Most imaging modalities used in modern human research are represented in the CNDA, including magnetic resonance (MR), positron emission tomography (PET), computed tomography (CT), nuclear medicine (NM), computed radiography (CR), digital radiography (DX), and ultrasound (US). However, the majority of the imaging data in the CNDA are MR and PET of the human brain. Currently, about 20% of the total imaging data in the CNDA is available by request to external researchers. CNDA's available data includes large sets of imaging sessions and in some cases clinical, psychometric, tissue, or genetic data acquired in the study of Alzheimer's disease, brain metabolism, cancer, HIV, sickle cell anemia, and Tourette syndrome.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Anonymization; Archive; Brain metabolism; CNDA; Cancer; Central Neuroimaging Data Archive; Controls; Data; Database; De-identify; HIV; Imaging; Informatics; JAAT; Multi-center; Multi-site; Neuroinformatics; Pipeline; Sharing; Sickle-cell anemia; Tourette syndrome; Washington University; XNAT.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Coats M, Morris JC. Antecedent Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease: The Adult Children Study. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2005;18:242–244. - PubMed
-
- Doran SJ, d’ Arcy J, Collins DJ, Andriantsimiavona R, Orton M, Koh D-M, Leach MO. Informatics in radiology: development of a research PACS for analysis of functional imaging data in clinical research and clinical trials. Radiographics. 2012;32:2135–2150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

