Intraoperative aortic dissection
- PMID: 26440240
- PMCID: PMC4881678
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-9784.166463
Intraoperative aortic dissection
Abstract
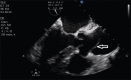
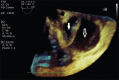
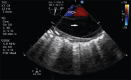
Intraoperative aortic dissection is a rare but fatal complication of open heart surgery. By recognizing the population at risk and by using a gentle operative technique in such patients, the surgeon can usually avoid iatrogenic injury to the aorta. Intraoperative transesophageal echocardiography and epiaortic scanning are invaluable for prompt diagnosis and determination of the extent of the injury. Prevention lies in the strict control of blood pressure during cannulation/decannulation, construction of proximal anastomosis, or in avoiding manipulation of the aorta in high-risk patients. Immediate repair using interposition graft or Dacron patch graft is warranted to reduce the high mortality associated with this complication.
Figures

References
-
- Still RJ, Hilgenberg AD, Akins CW, Daggett WM, Buckley MJ. Intraoperative aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Surg. 1992;53:374–9. - PubMed
-
- Hwang HY, Jeong DS, Kim KH, Kim KB, Ahn H. Iatrogenic type A aortic dissection during cardiac surgery. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010;10:896–9. - PubMed
-
- De Smet JM, Stefanidis C. Acute aortic dissection after off-pump coronary artery surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2003;24:315–7. - PubMed
-
- Hirose H, Svensson LG, Lytle BW, Blackstone EH, Rajeswaran J, Cosgrove DM. Aortic dissection after previous cardiovascular surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004;78:2099–105. - PubMed
-
- Reinke RT, Harris RD, Klein AJ, Daily PO. Aortoiliac dissection due to aortic cannulation. Ann Thorac Surg. 1974;18:295–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
